Import and Classify
Import the TSurf model and classify the components.
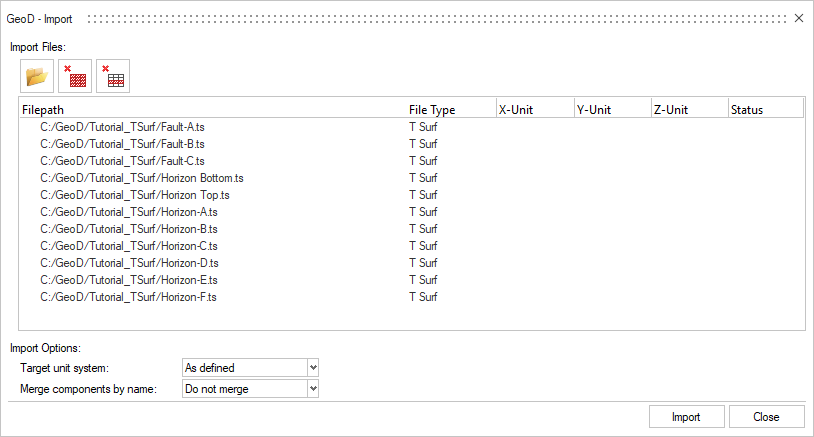
Import pre-made surfaces (tsurfs in this tutorial) and/or points (a csv file here) to define the model domain. The individual tria(ngular) or quad(rilateral) elements making up the surfaces are often called 2D or shell elements.
Import
Import the TSurf model.
Classify Model
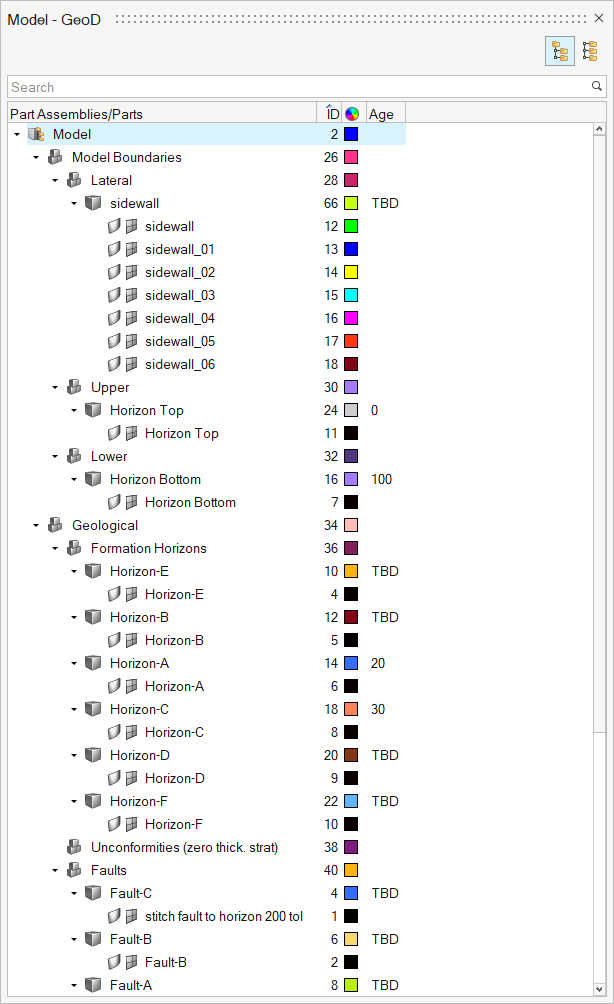
Use Classify tool to classify TSurf model and its components.
After import it is necessary to classify and date the imported surfaces. The classification and age assignment provides the logical basis for subsequent clean-up operations. Whilst these operations can be applied on unclassified or undated features, the geological rules underlying them are not employed and unexpected results may occur.