Laminar Couette Flow with Imposed Pressure Gradient
In this application, AcuSolve is used to simulate the viscous flow of water between a moving and a stationary plate with an imposed pressure gradient. AcuSolve results are compared with analytical results described in White (1991). The close agreement of AcuSolve results with analytical results validates the ability of AcuSolve to model cases with imposed pressure gradients.
Problem Description
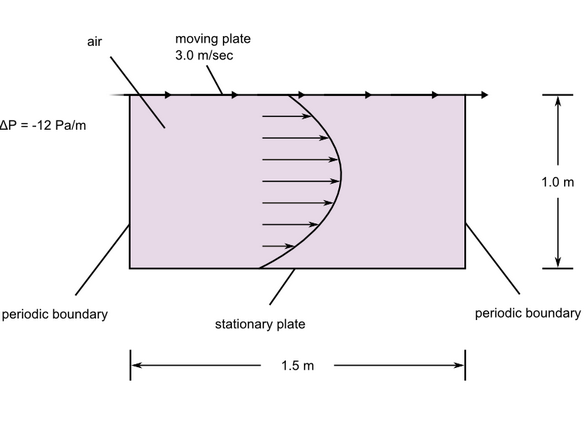
Figure 1. Critical Dimensions and Parameters for Simulating Laminar Couette Flow with an Imposed Pressure Gradient
Figure 2. Mesh used for Simulating Laminar Couette Flow with an Imposed Pressure Gradient
AcuSolve Results
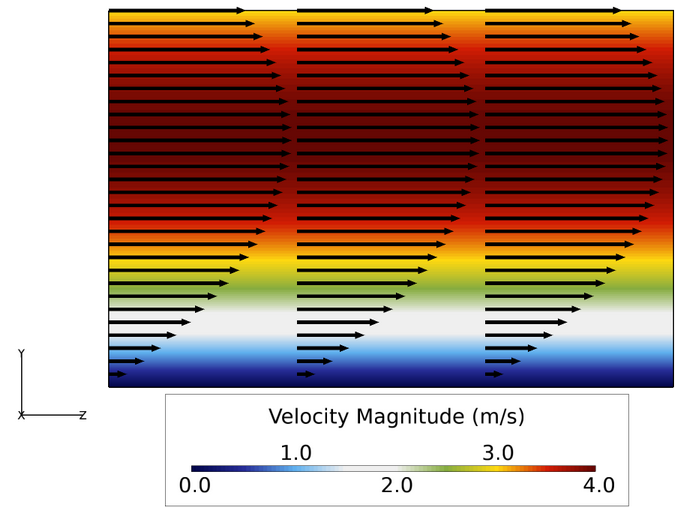
Figure 3. Z-Velocity Contours and Velocity Vectors
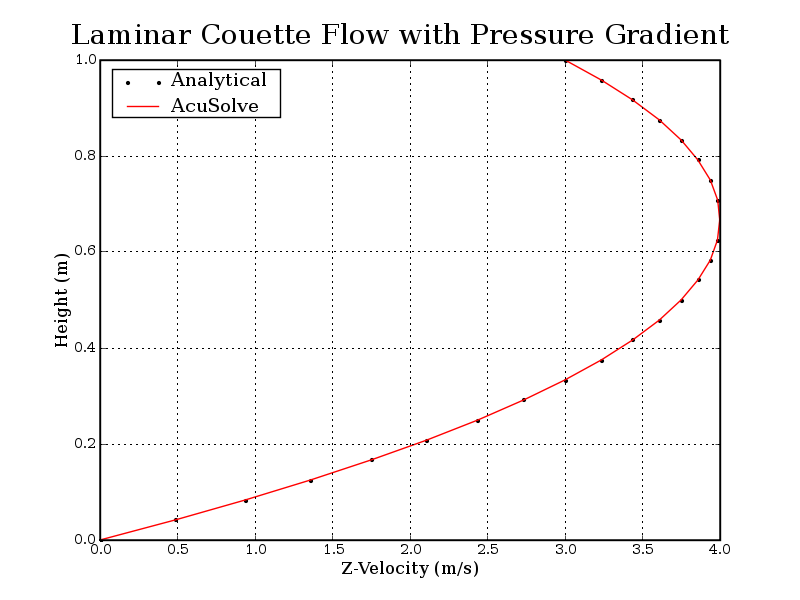
Figure 4. Z Velocity Plotted Against Height Above the Bottom of the Flow Field (Z Velocity is Presented on the X Axis to Better Represent the Velocity Profile in the Direction of Flow)
Summary
The velocity profile computed by AcuSolve agrees well with the analytical solution for this application. The velocity profile arises due to the combination of the imposed pressure gradient and the constant upper-wall velocity. Note that the combination of these effects results in the asymmetric velocity profile that is reflected in the results.
Simulation Settings for Laminar Couette Flow with Imposed Pressure Gradient
AcuConsole database file: <your working directory>\couette_flow\couette_flow.acs
Global
- Problem Description
- Analysis Type - Steady State
- Turbulence equation - Laminar
- Auto Solution Strategy
- Relaxation factor - 0.2
- Material Model
- Air
- Density - 1.0 kg/m3
- Viscosity - 1.0 kg/m-sec
- Air
- Body Force
- DP/DL
- Gravity
- Z-component - 18.0 m/sec2
- Gravity
Model
- DP/DL
- Volumes
- Fluid
- Element set
- Material model - Air
- Body force - DP/DL
- Element set
- Fluid
- Surfaces
- Max_X
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Type - Symmetry
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Max_Y
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Type - Wall
- Wall velocity type - Cartesian
- Z-velocity - 3.0 m/s
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Max_Z
- Simple Boundary Condition - (disabled to allow for periodic conditions to be set)
- Min_X
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Type - Symmetry
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Min_Y
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Type - Wall
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Min_Z
- Simple Boundary Condition - (disabled to allow for periodic conditions to be set)
- Max_X
- Periodics
- Periodic 1
- Periodic Boundary Conditions
- Type - Periodic
- Periodic Boundary Conditions
- Periodic 1
References
F. M. White. "Viscous Fluid Flow". Section 3-2.3. McGraw-Hill Book Co., Inc.. New York. 1991.