SS-T: 2040 Joints
Create joints in SimSolid.
Purpose
- Learn how to create joints - hinge, linear guide, and virtual pins.
Model Description
- Joints_Hinge_LinearGuide.ssp
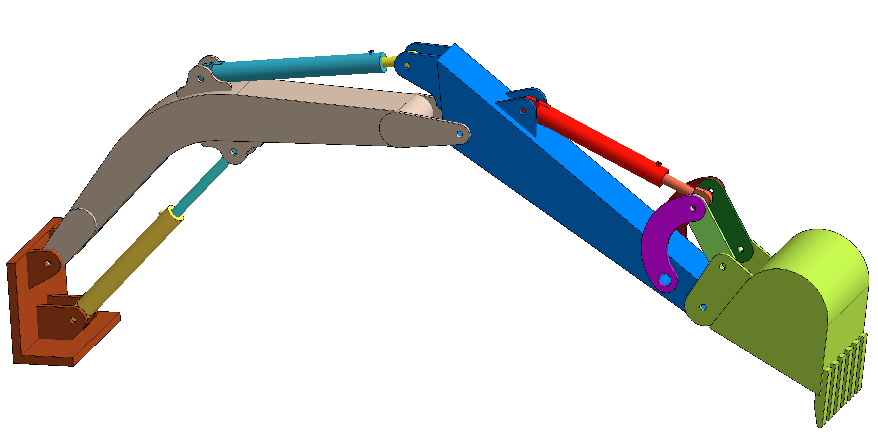
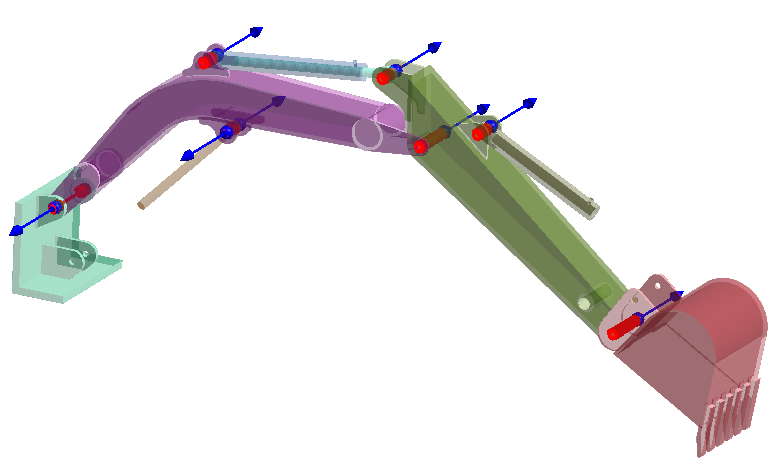
Figure 1.
- Material is set to Steel for all parts.
- Modal analysis is pre-defined.
Open Project
Open the SimSolid project file.
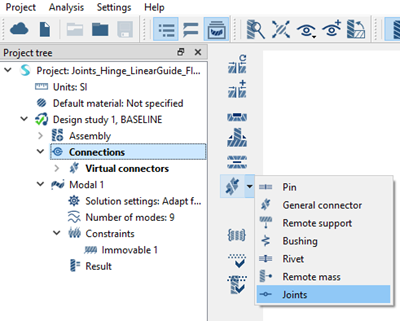
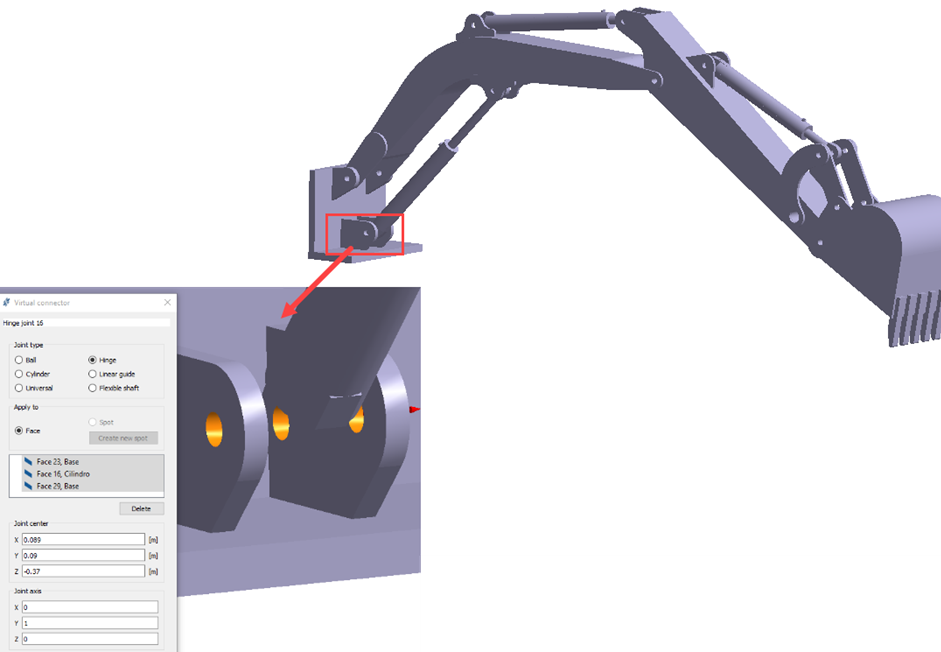
Create Hinge Joints
Create hinge joints on selected faces.
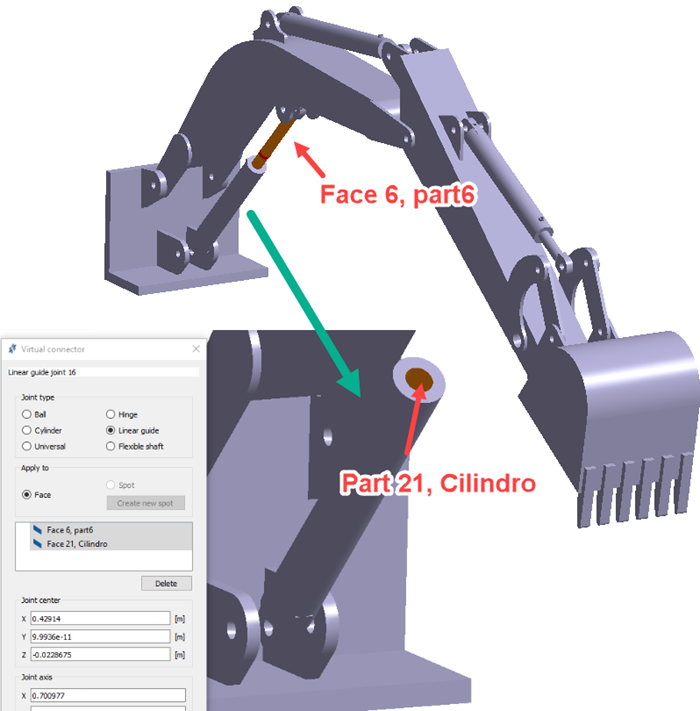
Create Linear Guide Joint
Create a linear guide joint on selected faces.
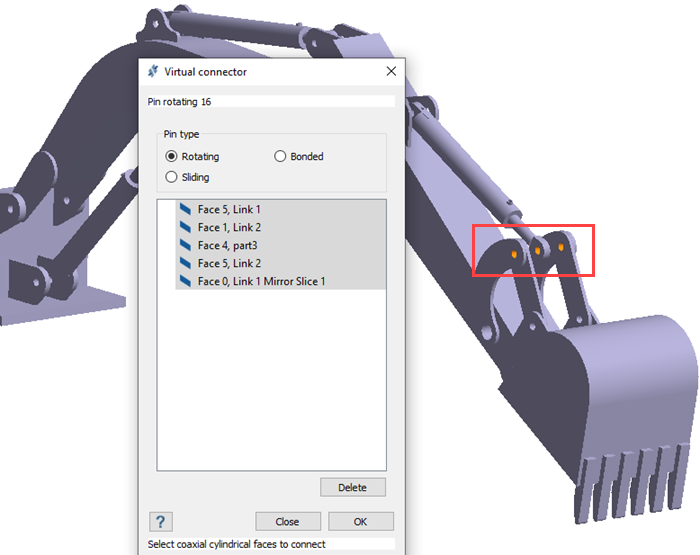
Create Virtual Pin
Create a virtual pin on selected faces.
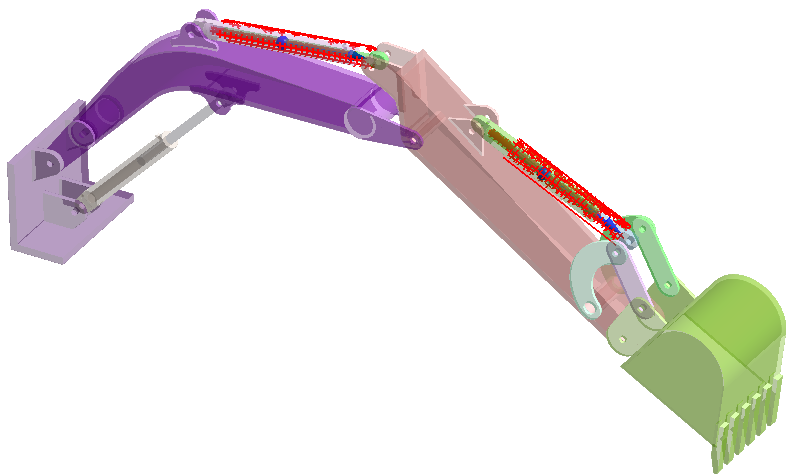
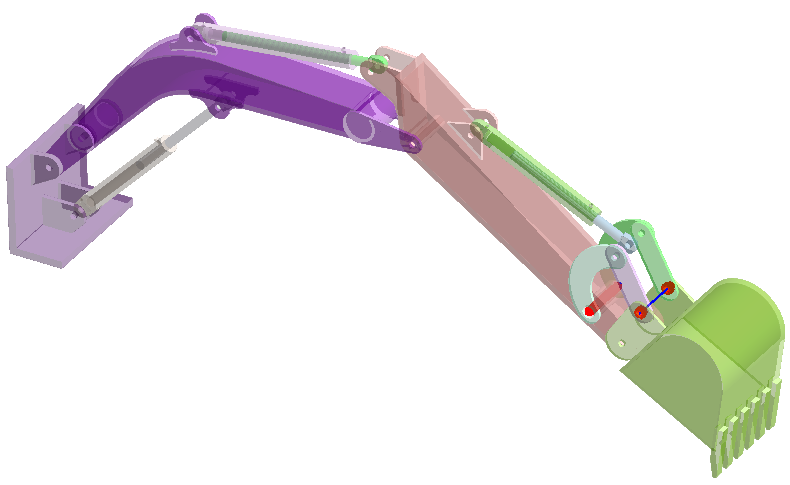
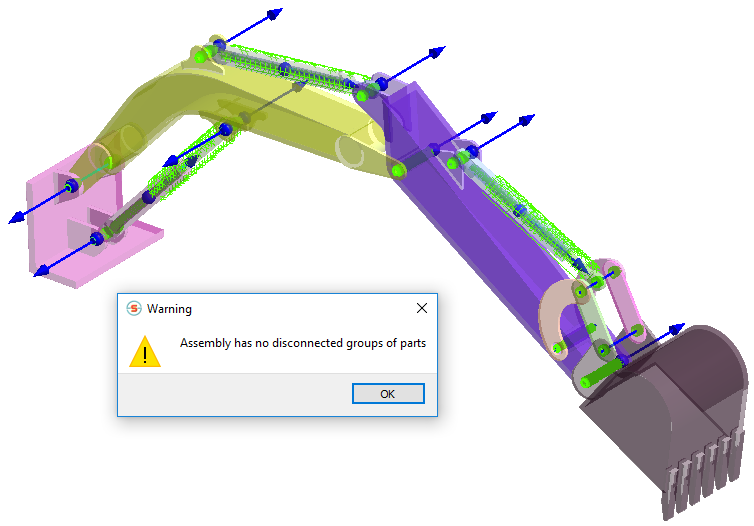
Review Connections
Find disconnected groups of parts in the model.
Run Analysis
Solve the analysis.
- In the Project Tree, open the Analysis Workbench.
-
Click
 (Solve).
(Solve).
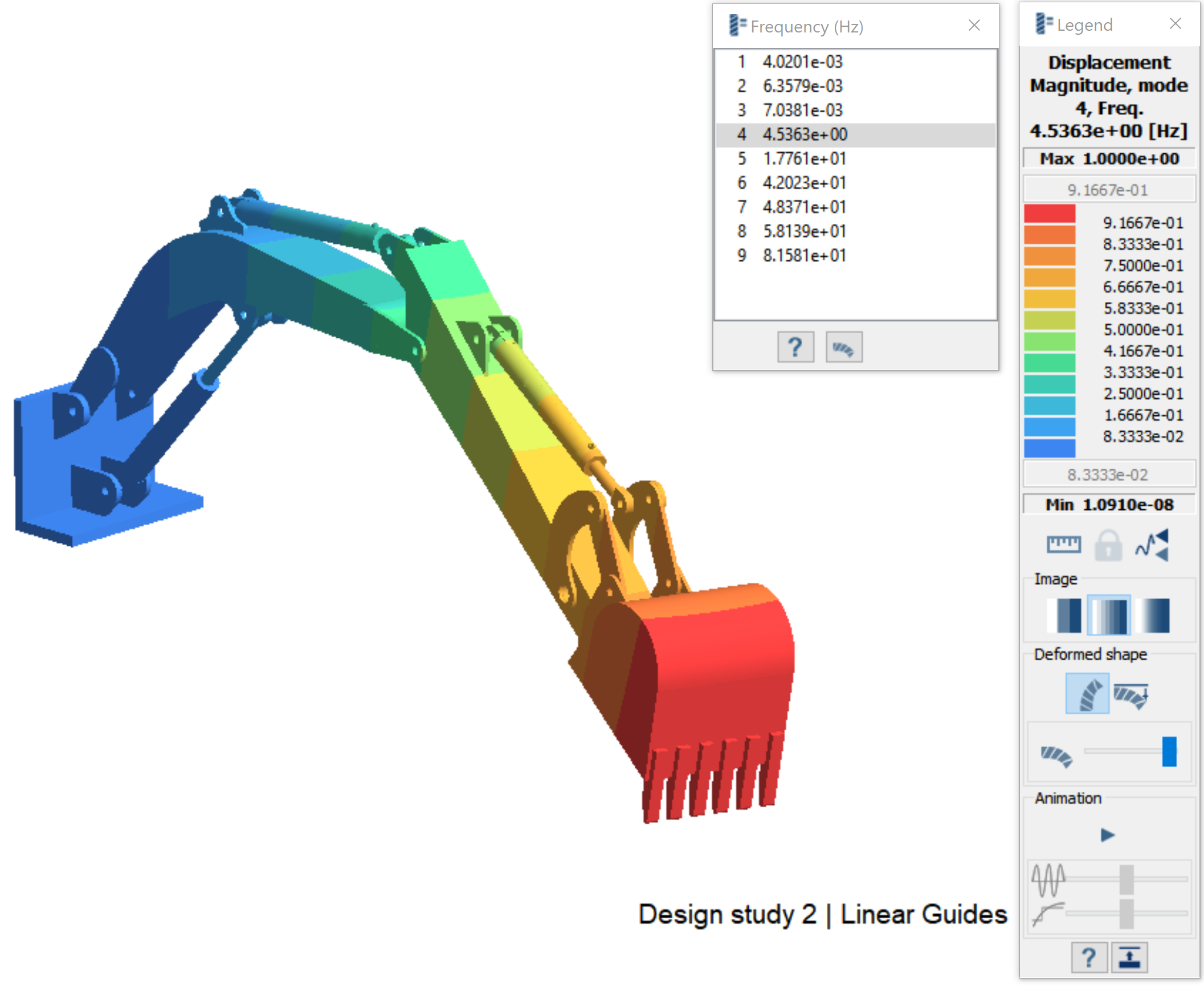
Review Results
Plot the displacement contour.