Calculating the Port Parameters and Field Data
Use the Multiport post-processing application macro in POSTFEKO to calculate the port reflections and field data for a model (plate4prt.fek) with different load configurations.
-
Open POSTFEKO and run the Multiport
post-processing
application macro from the application macro library.
The Multiport post-processing dialog is displayed.
-
Specify the input method for the Multiport
post-processing
application macro.
For this example, a Feko model (plate4prt.fek) is used as input.Tip: Find the examples in the <FEKO_SHARED_HOME> directory:
%FEKO_SHARED_HOME%/installedapplicationmacrolibrary/POSTFEKO/MultiportCalculation/examples.
- Under Definition method, select Feko model.
-
In the Model field, browse to the file location
of plate4prt.fek.
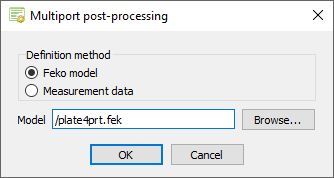
Figure 1. The Multiport post-processing dialog. - Click OK to close the Multiport post-processing dialog.
The Processing options dialog is displayed. -
Specify the processing options and data handling.
- Under Port (source and load) information, select Specify using dialogs.
- Under Data handling, select Replace stored data (if they exist).
- Under Export options , clear the Export generated results (*.ffe,*.hfe,*.efe,*.pfs) check box.
- [Optional] Under Export options, select the Export scaling coefficients (*.xml, *.mat) to export the scaling coefficients to file.
- [Optional] Under Additional options, select Add reference impedance to verify the model setup.
- [Optional] Under Additional options, select Add reference impedance (Z0) in calculations to
- [Optional] Under Additional options, select Subtract source loading (move the reference plane before the source load) to verify the model setup.
- Under Additional options, select Calculate scaled fields and currents to calculate the scaled fields and currents.
- [Optional] Under Additional options, select Save settings to file (*.lua) to save the multiport settings to file.
-
[Optional] In the Results prefix (optional)
field, specify a results prefix to group the calculated results in
POSTFEKO.
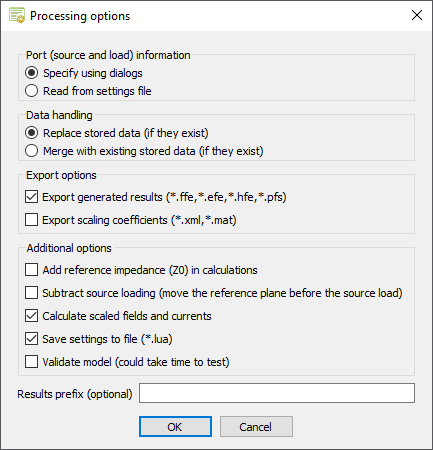
Figure 2. The Processing options dialog. - Click OK to close the Processing options dialog.
The Select ports to load dialog is displayed. -
Specify the non-active (terminated) ports.
For this example, only Port_3 and Port_4 are non-active (terminated) ports.
- Clear the Port_1 check box.
- Clear the Port_2 check box.
-
Under Load specification type, select
Point loads (multiple 1-port loads of varying
types) to specify the individual loads.
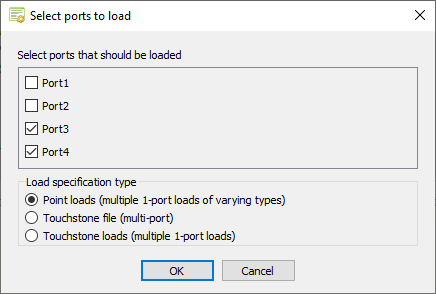
Figure 3. The Select ports to load dialog. - Click OK to close the Select ports to load dialog.
The Load type for terminated ports dialog is displayed. -
Specify the load types for the non-active (terminated) ports.
- In the Load type for port Port_3 field, select Complex load.
-
In the Load type for port Port_4 field, select
Complex load.
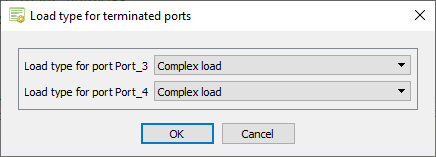
Figure 4. The Load type for terminated ports dialog. - Click OK to close the Load type for terminated ports dialog.
The Select load parameters dialog is displayed. -
Specify the load values for the non-active (terminated) ports.
-
Under Port_3 (Complex impedance), specify the
following values in Ohm:
- Real component: 25
- Imaginary component: 30
-
Under Port_4 (Complex impedance), specify the
following values in Ohm:
- Real component: 75
- Imaginary component: 0
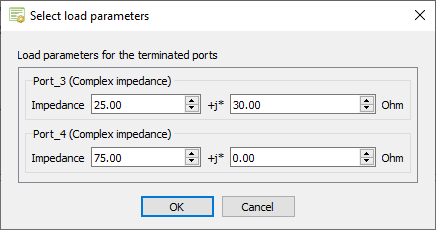
Figure 5. The Select load parameters dialog. - Click OK to close the Select load parameters dialog.
The Select source parameters dialog is displayed. -
Under Port_3 (Complex impedance), specify the
following values in Ohm:
-
Specify the excitations for the active ports and the load impedances.
-
Specify the excitation for Port_1.
- Under Port_1, in the Definition method drop-down list, select Direct connection.
- Specify the following values:
- Amplitude: 1 V
- Phase: 0°
-
Specify the excitation for Port_2.
- Under Port_2, in the Definition method drop-down list, select Direct connection.
- Specify the following values:
- Amplitude: 2 V
- Phase: 0°
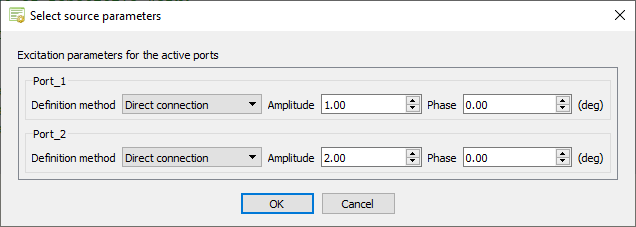
Figure 6. The Select source parameters dialog - Click OK to close the Select source parameters dialog.
The new results are calculated and available in POSTFEKO in the Project Browser under Stored data.
Figure 7. The multiport results under Stored data. -
Specify the excitation for Port_1.
-
[Optional] Run the plate4prt_example1_reference.cfx in
CADFEKO, load the
plate4prt_example1_reference.fek in the
plate4prt.pfs session and compare the results to the
Solver.
The field data is compared as calculated by the Multiport post-processing application macro to the solution obtained by the Solver, see Figure 8 and Figure 9.
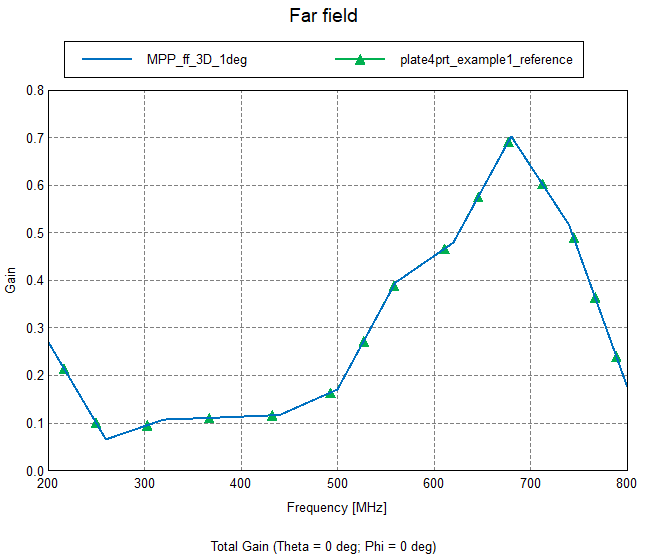
Figure 8. Comparison of near field values as a function of frequency at an arbitrary position.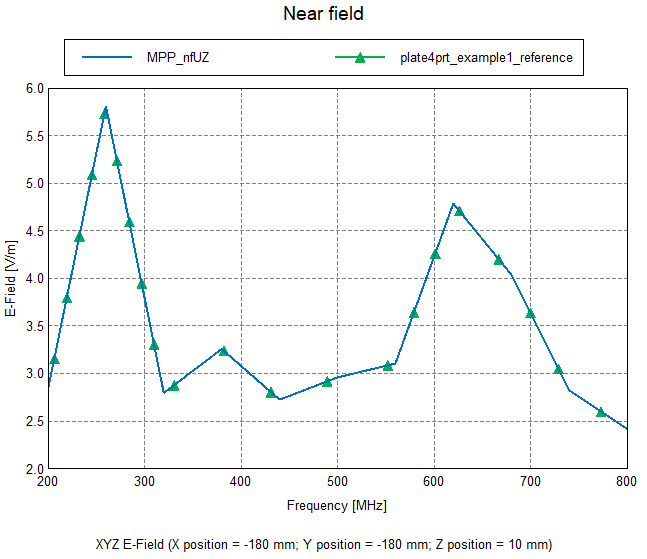
Figure 9. Comparison of far field gain over frequency in an arbitrary direction.