Perform Queries on Result Types-Interactive Mode
Once the results have been loaded in HyperMesh, use this tool to perform all types of queries on each result type stored in the result files, such as multiple load cases, components, different layers and systems.
Restriction: Only available in the Nastran, OptiStruct, Abaqus and ANSYS user profiles.
- From the menu bar, click Aerospace > Results > Results Query.
- Select Interactive.
-
Click Start.
A new dialog opens, and all of the available (native and derived) load cases are displayed.
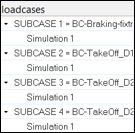
Figure 1. -
Use the arrows to view relevant file IDs that the subcases/simulation are
from.
This is useful in cases where the same subcase ID is present in multiple subcases.
-
Select one or more entries from the loadcases.
The data type entry is populated. The data types shown are based on the intersection among the common ones from the selected loadcases.
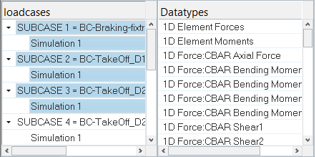
Figure 2. -
Select one data type for each query.
Once the data type is selected, related data components, layers, corners, the average method and systems are populated.
- Data Type [single selection per query]
- Data Component [multiple selection per query]
- Layer [multiple selection per query]
- Corner Data [single selection per query, default = centroid+corner nodes]
- Averaging Method [single selection per query, default = none]
- System [single selection per query, default = analysis system]
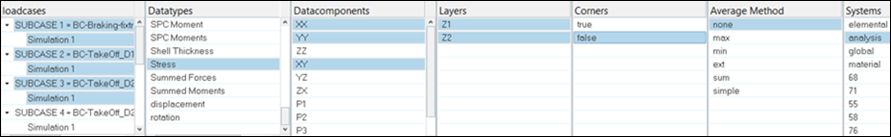
Figure 3. -
You can select multiple data components, multiple layers, single corner option,
single average method and single system.
Note: The system ID cannot be created or selected on the fly.
-
After the setup is complete for the data, click Set to
create a new query entry.
The following options are available for each query:
- Export
- You can have multiple query items and decide what to finally export among those available.
- ID
- The ID is generated, and cannot be changed.
- Entity Type (elements/nodes)
- Is automatically set up based on the binding among query setting and available entities.
-
Make your selection in the Selection By field.
The number of selections is generated based on what you selected for Selection By. If you selected All, the widget is not active. For all of the other choices, by clicking in the blank entry cell, the panel selection relative to either entity, component or set selection opens.
- Make your selection in the Sorting field.
-
Make your selection in the Organize Output field.
Organize output controls the writing of data if there are multiple load cases.
- Complex filter is used to select to export either the real or the imaginary part of the data.
- Output file is used to select the file where the data will be stored (.csv format). The same file entry can be used for different queries. In this case, result blocks will be appended.
- Click Settings to set up the result precision and the separator for the CSV.
- Select one of the newly created rows to open the list that shows which selection is bound to that particular query. The selection cannot be changed for that item, but is used to create a new one.
- Right-click on the numbers on the left-hand side of the dialog once the queries are selected to display a context menu to either duplicate or delete these items.
-
Click Apply to run the
realization of the query items in the defined output files.
When the report is complete a message displays in the lower-left corner. In the same area, other warning messages may display to notify you if there are any mistakes in the entries. The files written out from the Results Query tool are organized.
- Click Save to store the query settings.
-
Select a folder where two files will be simultaneously stored.
The queryconfig.tcl will be used in the batch mode to implement the loading of model/result sets for the creation of the result entity, while the queryconfig.xml is the main file storing all query set up from the interactive mode. These files can be modified by changing global or local settings for each query.