Model Entities
Learn more about MotionView model entities.
- Control Entities
-
- ControlSISO
- SolverDiff
- Geometric Entities
-
- Graphics
- Marker
- Point
- Vector
- Physical Entities
-
- Advanced Joints
- Beam
- Body
- Bushing
- Coil spring/Torsion spring
- Constraint
- Contact
- Coupler
- Field
- Force
- Gear
- Joints
- Motion
- Polybeam
- Sensors
- Spring Dampers
- Reference Entities
-
- Curve
- Deformable Curve
- Deformable Surfaces
- Materials
- SolverArray
- SolverString
- SolverVariable
- Surfaces
- User-Defined Entities
-
- Dataset
- Form
- Procedure
- Template
| Entity Properties | The attributes of an entity are called properties. The properties of a point entity are the X coordinate, Y coordinate, and Z coordinate. Body entities have mass and inertia properties. A property can be a simple scalar value or it can be a mathematical expression that makes a property a function of other properties in the model. |
| Entity Pairs | MotionView can store entities as pairs and provides
tools for managing symmetry. Each side of a symmetric model is separately maintained
to avoid having to build one half of a model and mirror it to create a full model.
Symmetry is turned on or off using the Symmetric Properties option.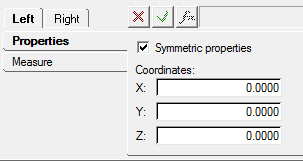 Figure 1. Points panel - Symmetric Properties option
Figure 1. Points panel - Symmetric Properties option |