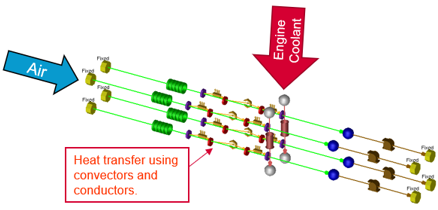
- Heat Input (Qin)
- Hot Fluid Delta.T
- Cold Fluid Delta.T
- Effectiveness
- Effectiveness vs Flow_Rate_Cold vs
Flow_Rate_Hot
Effectiveness is obtained from User Defined
Input for Effectiveness as function Flow_Rate_Cold and
Flow_Rate_Hot.
- Effectiveness vs NTU vs Heat Capacity Ratio
Effectiveness is
obtained from User Defined Input for Effectiveness as function NTU and
Heat Capacity Ratio.
UA is calculated from Constant user input or from
curve specified for Nusselt Number as function of Reynolds Number Cold
and Reynolds Number Hot
- Nusselt Number vs RE_Cold vs RE_Hot
Nusselt Number is
obtained from User Defined Input for Nusselt Number as function of
Reynolds Number Cold and Reynolds Number Hot
- Constant hA Coefficient value
NTU Effectiveness Methods:
- Cross Flow Unmixed
- Counter Flow
- Parallel Flow
- Cross Flow Both Side Mixed
- Cross Flow One Side Mixed
Cmin is mixed:
Cmax is mixed:
- Hs Parameter Methods (Constant and vs Hot and Cold
Flowrates)
The Hs parameter is typically used to describe
radiators where the hot side is a liquid coolant, and the cold side is
air.
A heat exchanger effectiveness can be calculated using
the Hs parameter.
Q is found using the effectiveness Qmax. The Q is
applied to the fluid streams to get the exit temperatures.