Maximize, Restore and Close a Window
When multiple windows are present, it is sometimes useful to maximize one window temporarily.
This can be done by clicking the  icon on
the current window toolbar. When the current window is maximized, the icon changes
to
icon on
the current window toolbar. When the current window is maximized, the icon changes
to  .
Clicking
.
Clicking  restores the window to its original size and location.
restores the window to its original size and location.
To close the current window, click  on the
window toolbar. Note that this icon does not control the visibility of the toolbar
in the window. When a window is closed, all of the visualization objects (surfaces,
rakes and annotations) in the closed window will be deleted. There is no undo
operation to recover visualization objects from a closed window.
on the
window toolbar. Note that this icon does not control the visibility of the toolbar
in the window. When a window is closed, all of the visualization objects (surfaces,
rakes and annotations) in the closed window will be deleted. There is no undo
operation to recover visualization objects from a closed window.
Showing/Hiding the Window Toolbar
The window toolbar is colored in green in the current window and beige in the non-current window(s). Its visibility can be controlled uniformly for all windows or individually for the current window. By default, the window toolbar is visible in all windows.
-
View menu commands to turn off the visibility of all window toolbars or just the current window toolbar are:
Multi-Window Examples
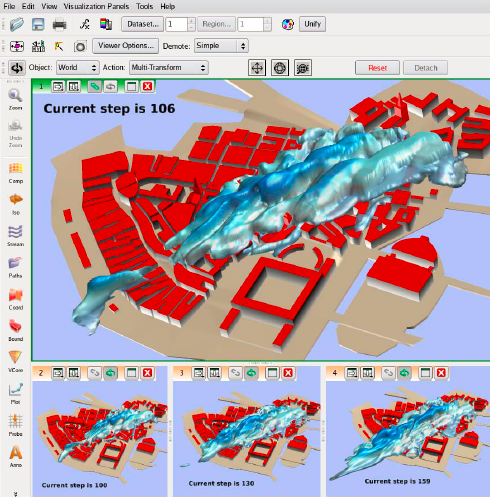
Figure 1. Multiple Views of a Transient Urban Dispersion Simulation
In the image above, visualization objects in the top window are created interactively, showing a dispersion cloud above a city. Creation of a new window as well as copying these visualization objects happens with a single mouse click. Transient sweeping can be applied to just one or all of the windows simultaneously to study how the dispersed cloud changes in time.
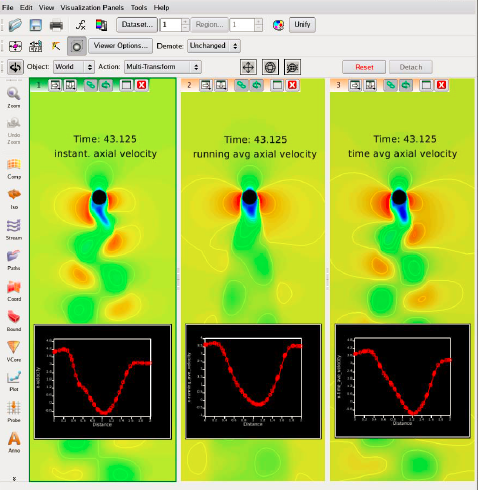
Figure 2. Vortex Shedding in Multiple Windows
There is no practical restriction on the number of windows which can be created. Also, the content of a window is not restricted in any way. In the image above, three windows display a coordinate surface and an embedded plot. A different scalar is illustrated in each of the three windows. You can sweep through time for all three windows simultaneously, updating all coordinate planes and embedded plots at the same time.