Drag Geometry
Drag surfaces, nodes, or lines along their normal direction, a vector, or another line.
Auto-Trim
Use the auto-trim ![]() option in the microdialog when dragging nodes and lines.
option in the microdialog when dragging nodes and lines.
While dragging lines or nodes, if a continuous surface or mesh is intersected and this option is ON, the newly created surfaces are trimmed at the intersection. The auto-trim option works for both geometry intersecting geometry and mesh. It also works for FE topology intersecting FE topology.
 Figure 2. Surfaces intersecting with surfaces
Figure 2. Surfaces intersecting with surfaces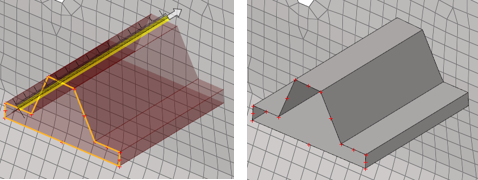 Figure 3. Surfaces intersecting with mesh
Figure 3. Surfaces intersecting with mesh
Figure 4.
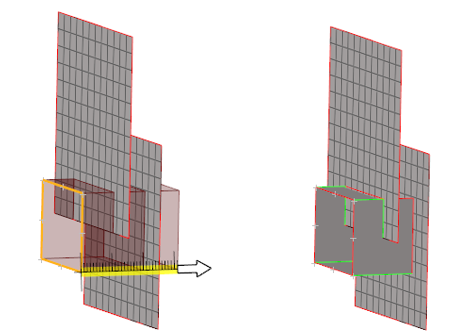
Figure 5.
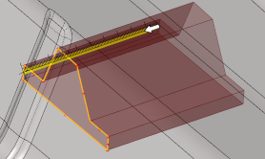 Figure 6. Input lines |
 Figure 7. Stitch trimmed surfaces ON |
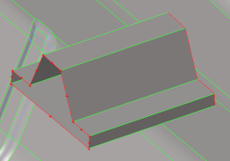 Figure 8. Stitch trimmed surfaces OFF |

 to define additional options.
to define additional options.