Feedback Traction Controller - PID Controller
A Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller is a feedback controller that computes a vehicle input using the error, the integral of error, and the rate of change of error between a desired vehicle response and the actual vehicle response.
To use a PID control you enter proportional (KP), integral (KI), and derivative (KD) gains, the type of desired response (for example, longitudinal speed or acceleration), and reference the desired response (for example, a table of speed vs time). The Altair Driver then applies the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control law to calculate the throttle and brake signals.
Algorithm
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Demand Signal | U |
| Feedback or response signal | X |
| Error | e |
| Proportional gain | Proportional gain |
| Derivative gain | Derivative gain |
| Integral gain | Integral gain |
| Integral control flag | Integral control flag |
| Integral band | Integral band |
| Driver throttle output | O throttle |
| Driver brake output | O brake |
| Drive Ratio | 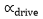 |
| Gear Ratio | 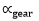 |
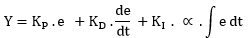
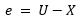
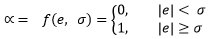
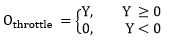
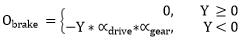
Types
- VELOCITY CONTROL - Demand signal is a velocity profile with time or distance traveled as independent variable.
- ACCELERATION CONTROL - Demand signal is an acceleration profile with time or distance traveled as independent variable.
- Demand signal can be constant, expression driver, user defined curve, or MotionView Signal (similar to Open Loop controller).
[LONG_PID_CONTROLLER]
TAG = 'PID'
TYPE = 'FOLLOW_VELOCITY'
DEMAND_SIGNAL = 'DEMAND_SPEED'
I_ACTIVE_BAND = 2
KP = 100
KD = 20
KI = 10
INITIAL_ERROR = -5| [FEEDFORWARD LONGITUDINAL CONTROLLER] | ||
|---|---|---|
| TAG | Attr - string | REQUIRED <PID > |
| Attr - string | OPTIONAL
|
|
| DEMAND_SIGNAL | Attr - string | REQUIRED Block name that contains the demand signal. See the Demand Signal Block topic to learn more about all of the available methods. |
| I_ACTIVE_BAND | Attr - real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KP | Attr - real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KD | Attr - real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KI | Attr - real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| INITIAL_ERROR | Attr-real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|