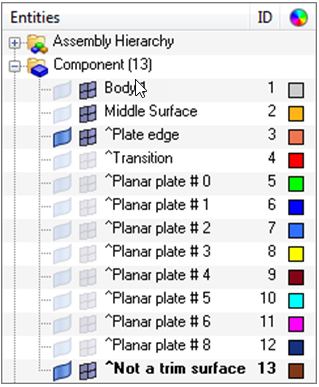
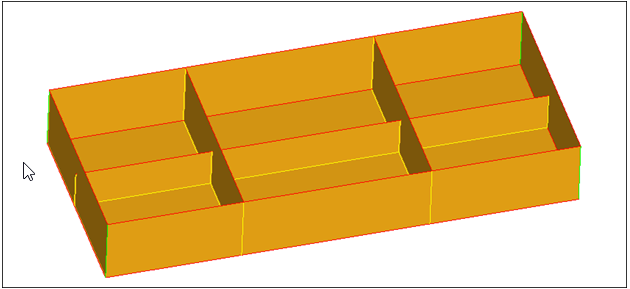
HM-2025: Auto-Midsurface with Advanced Extraction
In this tutorial you will use auto-midsurfacing with advanced extraction options.
- Use the offset+planes+sweeps option when midsurfacing
- Manually correct gaps in an auto-generated midsurface using the plates edit function
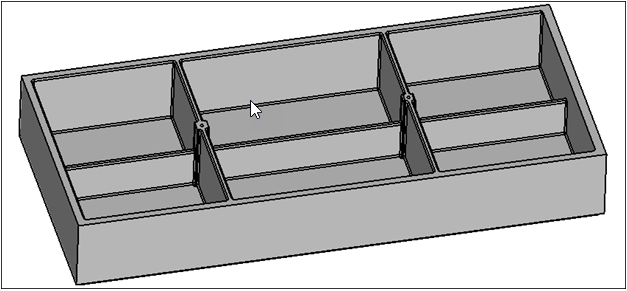
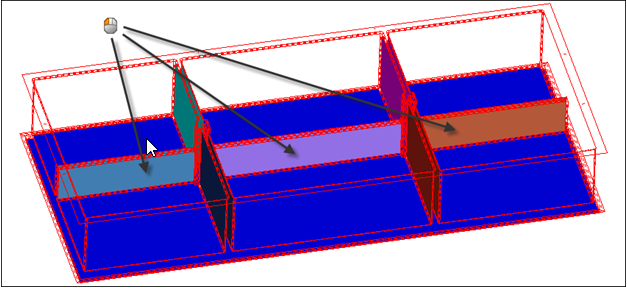
In this tutorial, you will be using CAD geometry data for a box with thin ribs inside of it. Because the geometry consists of thin planar sections, it is assumed that it will be modeled for FEA as shell elements. The elements will be created on the mid-planes of each section.
This exercise uses the Insert_planes.hm file, which can be found in the hm.zip file. Copy the file from this directory to your working directory.
Open the Model File
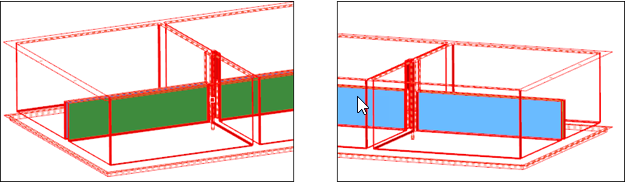
In this step you will open and view the model file.
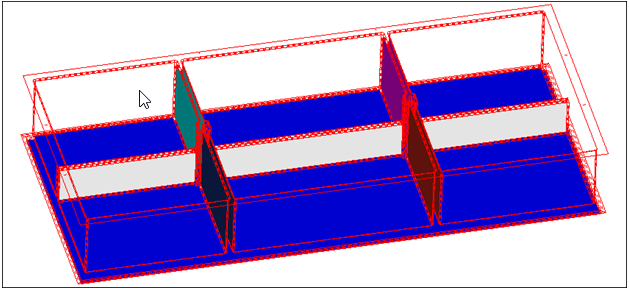
Resolve Midsurface Gaps
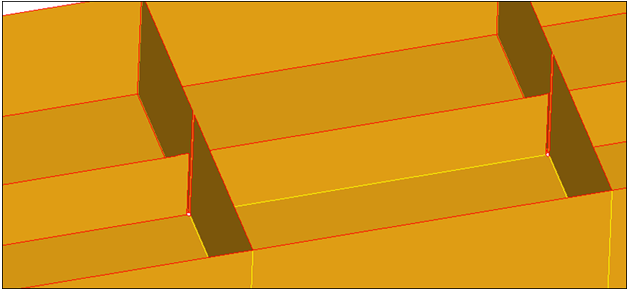
In this step you will use the edit plates subpanel to resolve midsurface gaps.
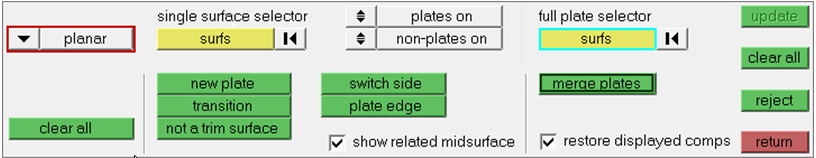
Use Plates Edit
In this step you will use plates edit to resolve remaining gaps.
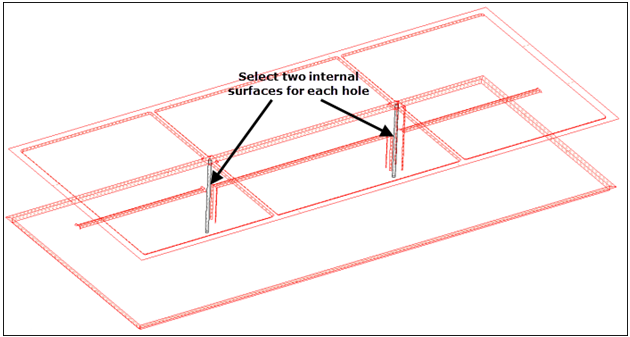
In this step you will need to tell the auto-midsurface algorithm not to trim the plates where the holes are located.
Save Your Work
In this optional step you will save your work.
This step is optional.
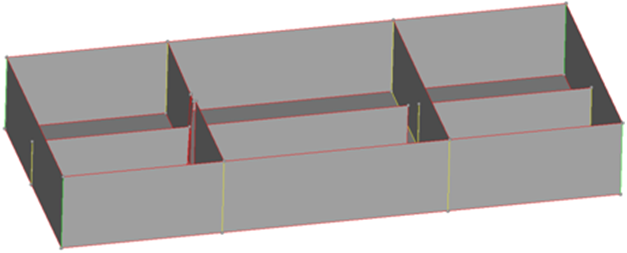
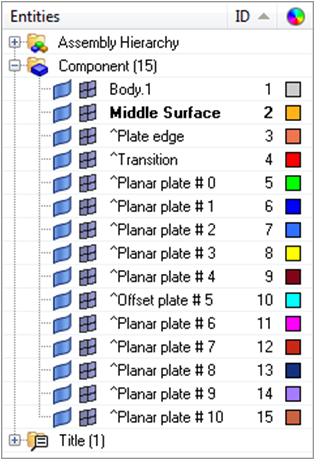
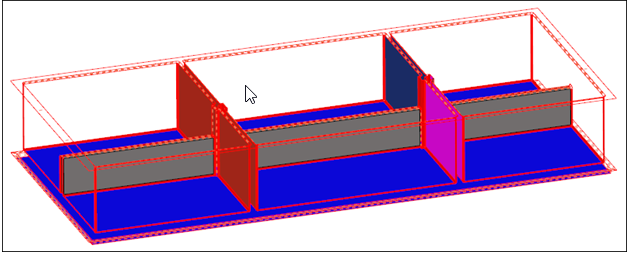
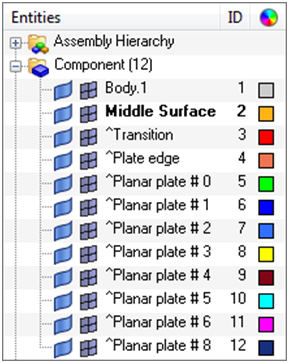
The model now contains surfaces on the mid-plane of the part. You used insert planes and plates edit to ensure that there were no erroneous gaps in the generated midsurfaces. You can now mesh these surfaces, or further modify their topology, depending on the requirements of the analysis.