Example 3: 14x14 Coaxial Feed Array with Uniform Algorithm
This case explains how to use the uniform algorithms to calculates the pointing parameters in a bidimensional coaxial feed array.
Step 1 Create a new MoM Project.
Open newFASANT and select File - New option.
Figure 1. New Project panel
Select MOM option on the previous figure and start to configure the project.
Step 2 Set the simulation parameters as shown.
Select Simulation - Parameters option, set the parameters and save it.

Figure 2. Simulation panel
Step 3 Create the array
First, select 'milimeters' on units list on the bar at the bottom of the main window.

Figure 3. The first element is created using Source - Coaxial Feed - Add Feed Point.

Figure 4. Add feed point
Select the surfaces and click on Add.

Figure 5. Coaxial Feed panel
Then save the feed point.
Use the array command and enter the characteristics of the array.

Figure 6. Array parameters

Figure 7. Array view
Step 4 Feed the array
To set the feeding of the array select Source - Antenna Feeding and the following panel will open.

Figure 8. Antenna Feeding panel
This is the default setting. To use the uniform algorithm click on Tools - User Function and select the corresponding function. NOTE To use the bi-dimensional uniform function it is needed to download both the bi-dimensional and the unidimensional functions.
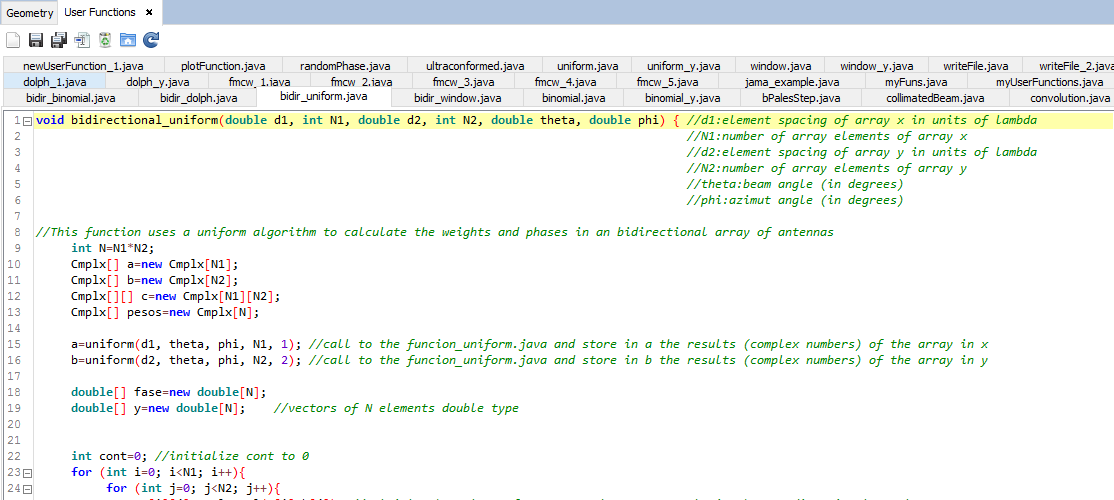
Figure 9. Bid-imensional Uniform function
A path has been selected by default so the files will be created on the mydatafiles folder in the newFASANT directory.

Figure 10. Bi-dimensional Uniform function
The next step is generating the text file. To do so click on Tools - Calculator and write the call to the function.

Figure 11. Calculator panel
The parameters to set are:
· d1 element spacing of the array in the x-axis in units of lambda
· N1 number of array elements of the array in the x-axis
· d2 element spacing of the array in the y-axis in units of lambda
· N2 number of array elements of the array in the y-axis
· theta beam angle, in degrees
· phi azimuth angle, in degrees
In this case, set the parameters as shown. Angles of theta=30º and phi=0º are selected as an example.

Figure 12. Calculator panel
A spacing of 0.5 in units of lambdas is selected because is equivalent to a spacing of 2.104 millimeters at 70 GHz.
The text file will be automatically generated in the mydatafiles folder.

Figure 13. Results file
Now, apply these results to the array created before by clicking on Source - Antenna Feeding.
The panel shown before will appear. To use the weights and phases calculated with the uniform algorithm, click on Import.
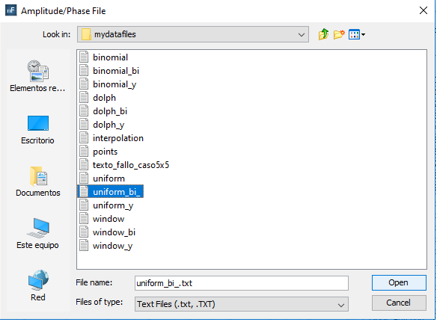
Figure 14. Amplitude/Phase File panel
Select the corresponding file and save the feeding.
Step 5 Solver parameters
Select Solver - Advanced Options and set the parameters as shown.

Figure 15. Solver Advanced Options panel
Step 6 Meshing the geometry model.
Select Mesh - Create Mesh to open the meshing configuration panel and then set the parameters as show the next figure.

Figure 16. Meshing panel
Step 7 Execute the simulation.
Select Calculate - Execute option to open simulation panel.

Figure 17. Calculate panel
Step 8 Show Results
The radiation cuts can be visualized by clicking on Show Results - Radiation Pattern - View Cuts.

Figure 18. Radiation Pattern Cuts
The radiation pattern can be visualized by clicking on Show Results - Radiation Pattern - View 3D Pattern.

Figure 19. Radiation Pattern 3D