Materials
Create or assign materials to the mold part cavity using the Materials Viewer.
Assign Materials
Materials are assigned from the Materials Database when the mold cavity is designated.
Create Materials
Customize a material and add it to My Materials.
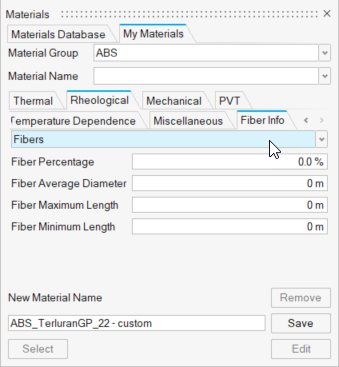
Add Fibers to Materials
Customize a material to include fibers and fiber orientation data.
Material Properties
The thermal, rheological, mechanical and PVT properties for materials are accessible from the Materials Viewer on the Materials Database tab.
Materials Database
The Materials Database tab provides the selection of materials available with Inspire Mold. The tab also provides access to the thermal, rheological, mechanical and PVT properties that you can review and modify for your model. Any modifications to materials are saved as new materials and accessed through the My Materials tab.Select a material with these options:
| Option | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Material Group | Provides of list of common materials available in the Materials Database. | |
| Material Name | Provides a list of common polymers of the chosen material. | |
Thermal Properties
Review the properties on the Thermal tab for the specified material:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat | Specifies the heat energy required to increase the temperature of a unit quantity (J/Kg·K). |
| Conductivity | Specifies the heat conductivity of the material (W/m·K). |
| Density | Specifies the density of the material (kg/m3). |
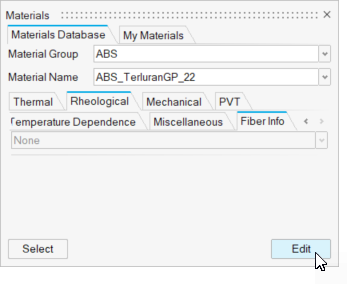
Rhealogical Properties
Review the properties on the Rhealogical tab for the specified material:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Constitutive Model | Four models are included in the Materials Database. Select the model
appropriate for your material choice. Review the Exponent, Consistency and Relative
Shear Stress for your chosen model.
|
| Temperature Dependence | Review the Williams-Landel-Ferry and temperature parameters:
|
| Miscellaneous | Review these parameters:
|
| Fiber Info | Review the fiber content for the specified material including:
Note: Some materials do not include fiber orientation data. To add this data,
edit an existing material and save it as a new material in the My Materials
tab.
|
Mechanical Properties
Review the properties on the Mechanical tab for the specified material:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus | Specifies the measure of the stiffness of the given material (Pa). |
| Poisson Ratio | Specifies the ratio of the relative contraction strain or transverse strain. |
| Yield Stress | Specifies the stress point at which the material deformation changes from elastic to plastic (Pa). |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Specifies the relative expansion divided by the change in temperature (1/K). |
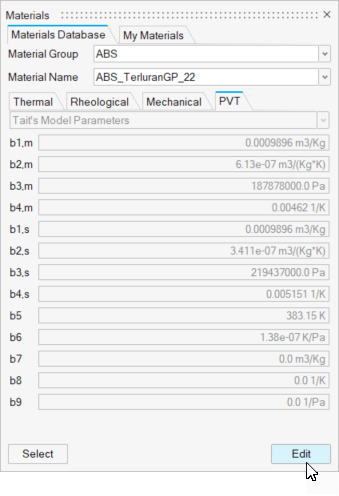
PVT Properties
Review the properties on the PVT tab for the specified material:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Tait's Model Parameters | Specifies the parameters to define a material's equation of state according to Tait's model (SI units). |
Example Exercise and Reference
Learn about material properties and walk through the steps to modify an existing material and save it as a new material.