From the Menu Bar, select Mesh Editing > Rigid Body > Check.
In the rigid body list, the green rigid bodies have a correct definition, the orange ones have to be checked, and the red ones have a bad definition. HyperCrash can automatically or semi-automatically correct the rigid bodies with errors or warnings.
A rigid body has a bad definition or must be checked if:
| • | The master node is master node of several rigid bodies. Check the column, 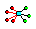 . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body is bad. . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body is bad. |
| • | The master node is on an element. Check the column,  . If there is a "y" in this column the rigid body is bad. . If there is a "y" in this column the rigid body is bad. |
| • | One or more slave nodes belong to another rigid body. Check the column, 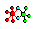 . If the number in this column is greater than 0, the rigid body is bad. . If the number in this column is greater than 0, the rigid body is bad. |
| • | The rigid body master node is also a slave node of another rigid body. Check the column, 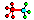 . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body has to be checked. . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body has to be checked. |
| • | The rigid body has one or zero slave nodes. Check the column, 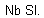 . If the number in this column is less than or equal to 1 (1 or 0), the rigid body is bad. . If the number in this column is less than or equal to 1 (1 or 0), the rigid body is bad. |
| • | In the same rigid body, if the master node is also selected as slave. Check the column, M=S. If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body is bad. |
| • | If a rigid body is small (small number of slave nodes and/or small size) and if the spherical inertia option is not activated in the rigid body definition. Check the column, 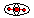 . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body has to be checked. . If there is a "y" in this column, the rigid body has to be checked. |
Correction
Master nodes in several rigid bodies
| 1. | Select a rigid body that has the master node in several other rigid bodies ("y" in the column,  ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click the right mouse button and, in the pop-up menu, select See Common Master of Rbodies to display the rigid bodies with common master nodes. |
| 4. | No automatic corrections are available in this version. |
Master node on an element
| 1. | Select a rigid body that has the master node on an element ("y" in the column,  ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click the right mouse button and, in the pop-up menu, select See Rbody Master on element(s) to display the element connected to the master node. |
| 4. | Click Save to automatically correct the rigid body. |
It becomes green.
The rigid body master node and the element node are disconnected. The rigid body master node is moved to the slave node center of gravity. The element node is included in the rigid body as slave.
Slave nodes in other rigid bodies
| 1. | Select a rigid body that has a slave node in other rigid bodies. (Number greater than 0 in the column,  ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click the right mouse button and, in the pop-up menu, select See slave nodes in other Rbodies to display in blue the slave nodes included in other rigid bodies. |
| 4. | Deselect those nodes using the following buttons:  , ,  , ,  , ,  , or , or  . . |
| 5. | Click Save to save the corrected rigid body. |
It becomes green if all the slave nodes in other rigid bodies are removed.
The rigid body master node is also slave node of another rigid body
| 1. | Select a rigid body with a master node which is also a slave node of another rigid body ("y" in the column,  ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click the right mouse button and, in the pop-up menu, select See Cascades of Rbodies to display the rigid bodies connecting the master node. |
| 4. | Select the rigid body where the slave node has to be deleted and click  to display it in the graphic window. to display it in the graphic window. |
| 5. | Deselect the node using the following buttons:  , ,  , ,  , ,  , or , or  . . |
| 6. | Click Save to save the corrected rigid body. |
Rigid body with one or zero slave nodes
| 1. | Select a rigid body that has one or zero slave nodes. ("1" or "0" in the column, 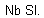 ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to delete it. to delete it. |
or
Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window.
to display the rigid body in the graphic window.
It becomes green.
In the same rigid body, the master node is also slave.
| 1. | Select a rigid body having its master node defined also as slave ("y" in the column, M=S). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click the right mouse button and, in the pop-up menu, select See Rbody Master is also slave to display the rigid body master node in blue. |
| 4. | Click Save to automatically correct the rigid body. |
It becomes green.
The master node is removed from the slave node list.
Small rigid body without spherical inertia option.
| 1. | Select a rigid body that has a small size and no spherical inertia option. ("y" in the column  ). ). |
| 2. | Click  to display the rigid body in the graphic window. to display the rigid body in the graphic window. |
| 3. | Click Save to automatically correct the rigid body. |
It becomes green.
The spherical inertia option is set in the rigid body definition.
Semi-automatic correction
| 1. | Click  to execute the previously defined steps semi-automatically. to execute the previously defined steps semi-automatically. |
| 2. | The first bad rigid body is automatically selected and displayed. |
| 3. | The error or warning message is displayed. |
| 4. | This loop continues until all rigid bodies are corrected. |








![]() to display the rigid body in the graphic window.
to display the rigid body in the graphic window.