Create Pretension Bolt
Create pretension loads in 1D and 3D bolts.
ANSYS: Create Pretension Bolt
Create pretension loads in 1D and 3D bolts of ANSYS models using the ANSYS PRETS179 element type.
Samcef: Create Pretension Bolt
Create and edit 1D and 3D pretension bolt loads and bolt sections.
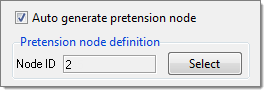
Create a 1D Pretension Bolt
A BOLT is created as a group entity.
The macro element ID for the first bolt that was created is written out as the maximum element ID in the model + the number of nodes present in model. 1000 is added to the macro element ID for consecutive bolts, that is, if the first bolt’s macro ID is 3, then the next bolt will be 1003 (3 + 1000).
The macro element ID of a bolt is reflected in its .SAI command, which is written along with the bolt’s corresponding output-code. It is preceded by the comment !!HM_TEMP_OUTPUTBLOCK, which enables the model-reader to ignore the output block upon import and not create any output blocks in HyperMesh. A bolt card that does not contain an output definition will not have a .SAI command written out.
All such commented commands are automatically exported out again upon re-export in the same format.
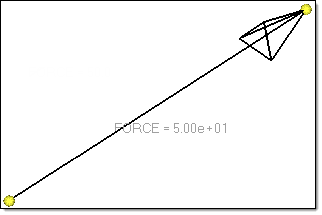
The load applied on a bolt is written out in the solver deck. A load’s magnitude is written out after VAL, and any curve attached to the load using Function Time is written after the keyword NF.
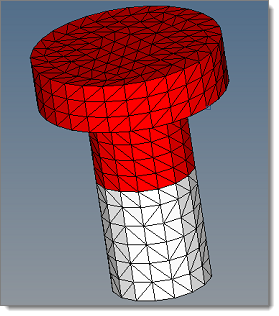
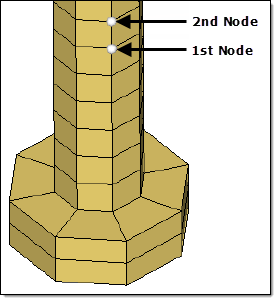
Create a 3D Pretension bolt
A BOLT is created as a group entity.
The macro element ID of the first bolt that was created is written out as the maximum element ID in the model + the number of nodes present in model. 1000 is added to the macro element ID for consecutive bolts, that is, if the first bolt’s macro ID is 117653, then the next bolt will be 118653 (117653 + 1000).
The macro element ID of a bolt is reflected in its .SAI command, which is written along with the bolt’s corresponding output-code. It is preceded by the comment !!HM_TEMP_OUTPUTBLOCK, which enables the model-reader to ignore the output block upon import and not create any output blocks in HyperMesh. A bolt card that does not contain an output definition will not have a .SAI command written out.
All such commented commands are automatically exported out again upon re-export in the same format.
The load applied on a bolt is written out in the solver deck. A load’s magnitude is written out after VAL, and any curve attached to the load using Function Time is written after the keyword NF.