PostgreSQLのインストールとコンフィギュレーション
PostgreSQLは、Postgresとも呼ばれる、拡張性と標準の準拠に重点が置かれた、オブジェクト関係データべース管理システムです。
PostgreSQLは、単一マシンの小さなアプリケーションからインターネット向け、またはデータウェアハウス向けの多くの同時ユーザーを有する大規模アプリケーションまで、さまざまな作業負荷を処理できます。ACIDに準拠し、トランザクションを行います。PostgreSQLは、更新可能ビューおよびマテリアライズドビュー、トリガー、外部キーを備え、関数およびストアドプロシージャをサポートし、その他の拡張性を提供します。
PostgreSQLは、多くの企業および個々のコントリビューターによる多様なグループである、PostgreSQL Global Development Groupによって開発されています。無償のオープンソースで、パーミッシブソフトウェアライセンスであるPostgreSQLライセンスの下でリリースされています。詳細は、https://www.postgresql.org/をご参照ください。
前提条件
システム要件
| プラットフォーム | 64ビット | 32ビット |
|---|---|---|
| Windowsバージョン | 2016、2012 R2およびR1、2008 R2、7、8、10 | 2008 R1、7、8、10 |
PostgreSQLインストーラー
次のインストーラーを使用して、PostgreSQL: postgresql-10.1-2-windows-x64.exeまたはこれ以降を設定します。PostgreSQLの実行ファイルは、HyperMeshソフトウェアのインストールの一部としてインストールされます。PostGresDBをインストールするための別のインストーラが表示されます。
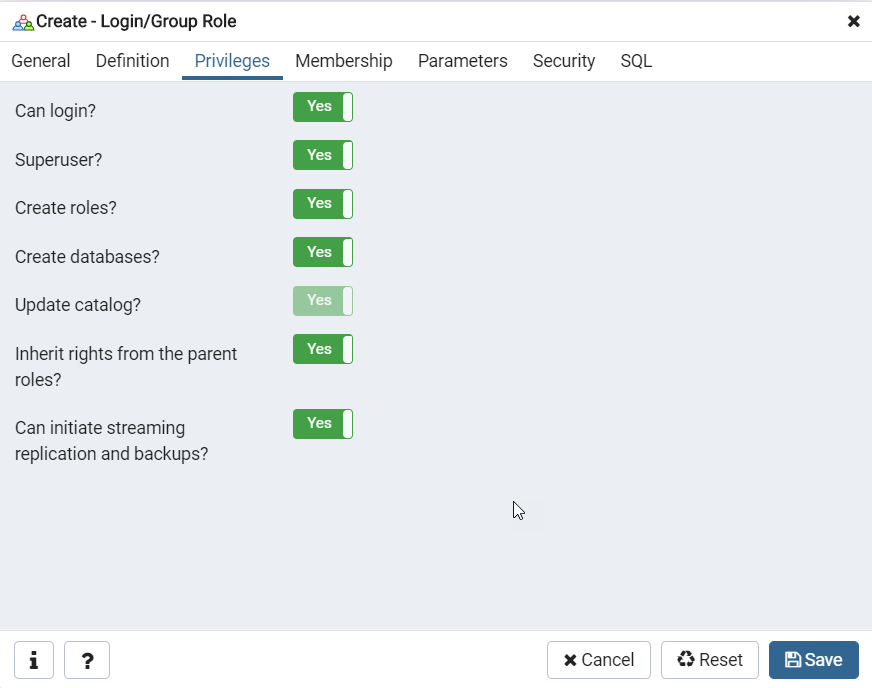
PostgreSQLのインストール
ここでは、PostgreSQLのインストール方法について学習します。
このインストールは、デフォルトの値およびオプションを使用して実行することをお勧めします。また、Windowsの管理パスワードの入力を求められたら、ご自身のWindowsパスワードを使用できます。
共有ライブラリへの接続
このタスクでは、PostgreSQL Shared Libraryに接続する方法について学習します。
-
共有ライブラリを作成するには、以下の手順に従います:
-
既存のライブラリを追加するには、以下の手順に従います: