Edit Surfaces
Each surface contains one or more faces. It is usually preferable to combine multiple faces into one surface entity before you use the meshing tools.
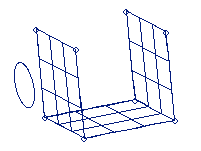
Figure 1. . A circle and a surface (represented with surface lines) before trimming.
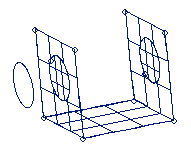
Figure 2. . After the circle is used to trim the surface, two new surfaces are created (shown highlighted) and the original surface is trimmed.
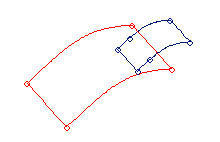
Figure 3. . Two surfaces before trimming.
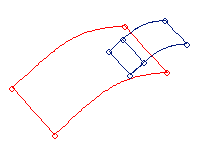
Figure 4. . The smaller surface is split into two surfaces after it is trimmed with the larger surface.