Result Types
Results are available for filling, packing, cooling, and warpage analysis stages.
Filling Results
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature |
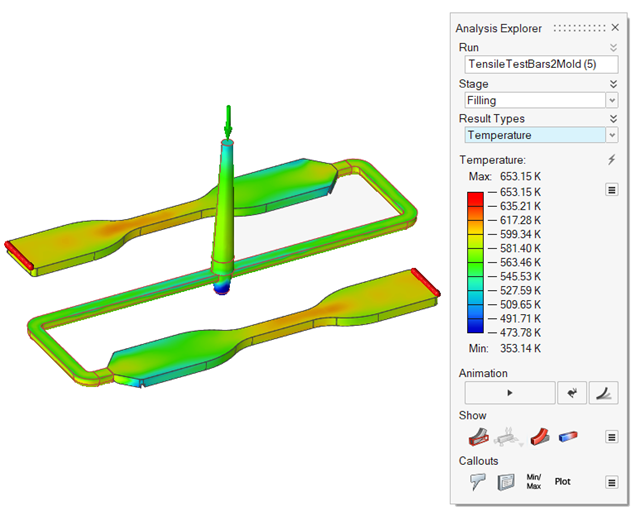 |
| Flow Front Temperature | Review the temperature at the time of filling.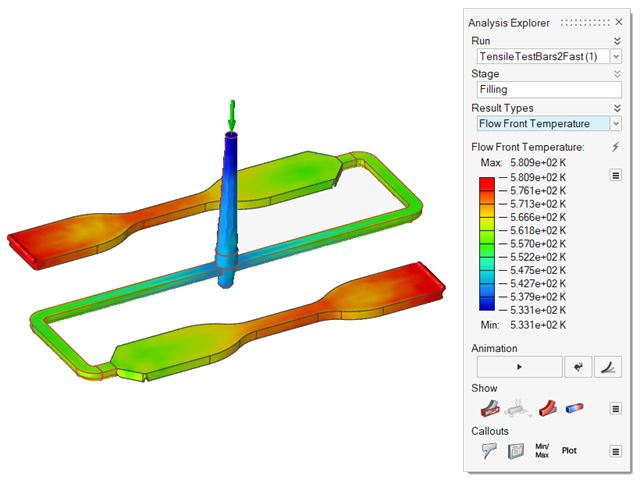 |
| Velocity |
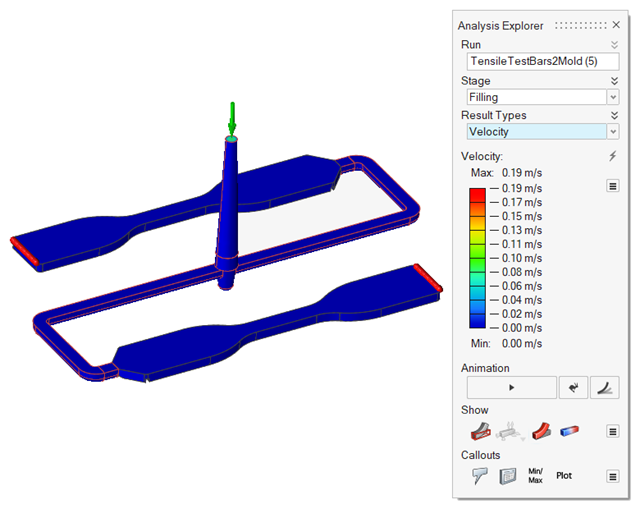 |
| Pressure | Review pressures inside the mold cavity produced during the
filling stage.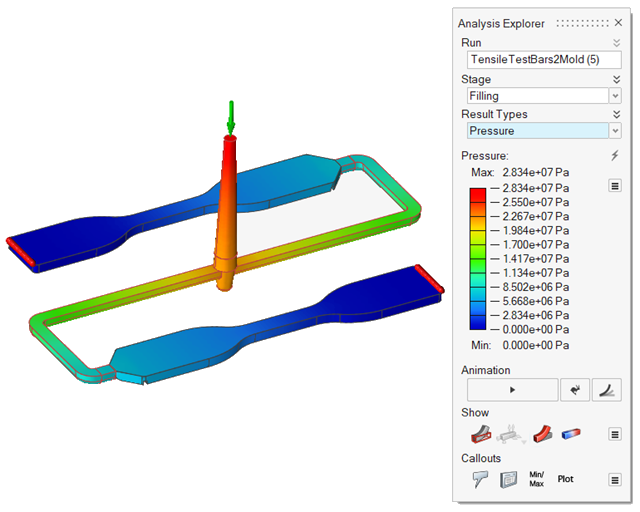 |
| Filling Time | Review the time it takes the material to reach different
areas within the part. The filling results can help you
determine the best way to fill the part and detect patterns that
indicate the potential for incomplete filling, unbalanced flow,
weld lines and air pockets.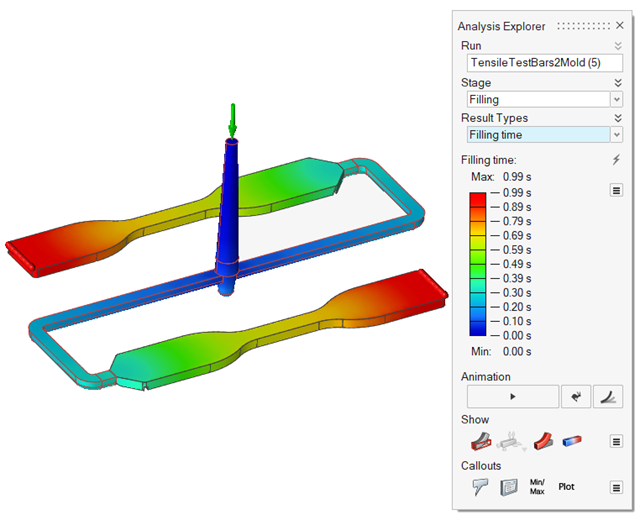 |
| Air Traps |
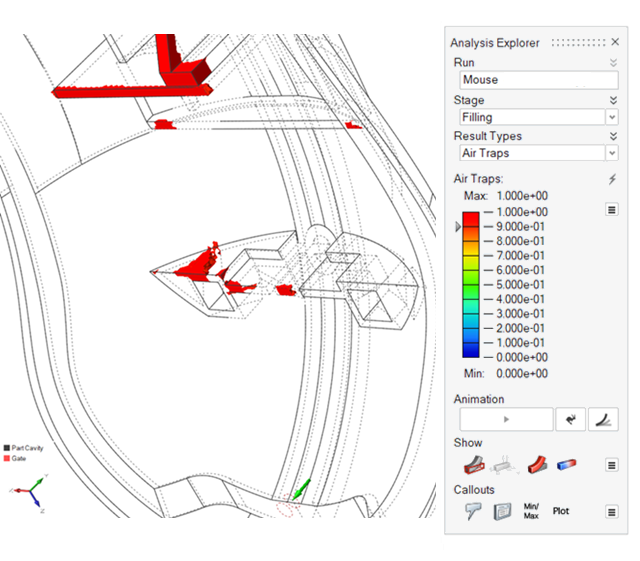 |
| Weld Lines | Locate regions during filling where two flow fronts meet.
Such regions may cause structural and cosmetic issues.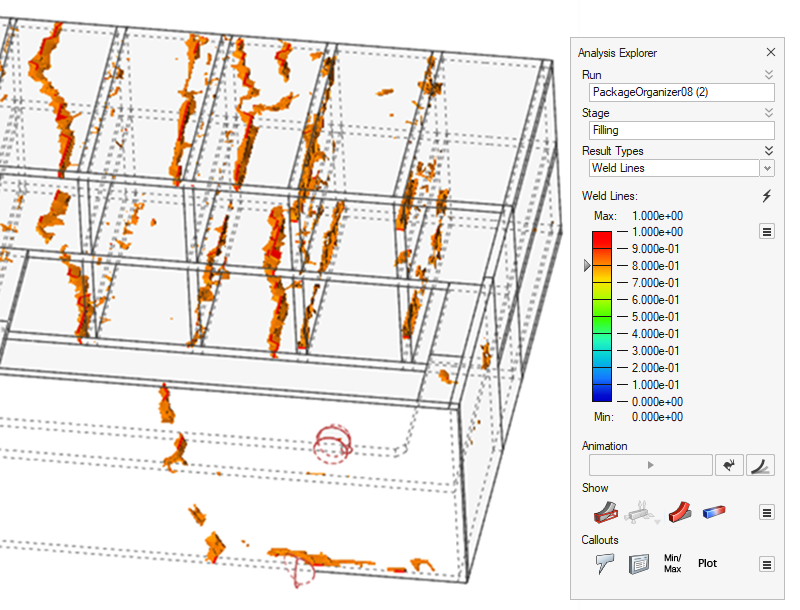 |
| Effective Strain Rate | Review the polymer's effective strain rate. The polymer's
viscosity is a strong function of its strain rate. This result
can help you understand the filling behavior of the polymer.
Additionally, if strain rate exceeds a certain threshold
(different for each material) the polymer may degrade. 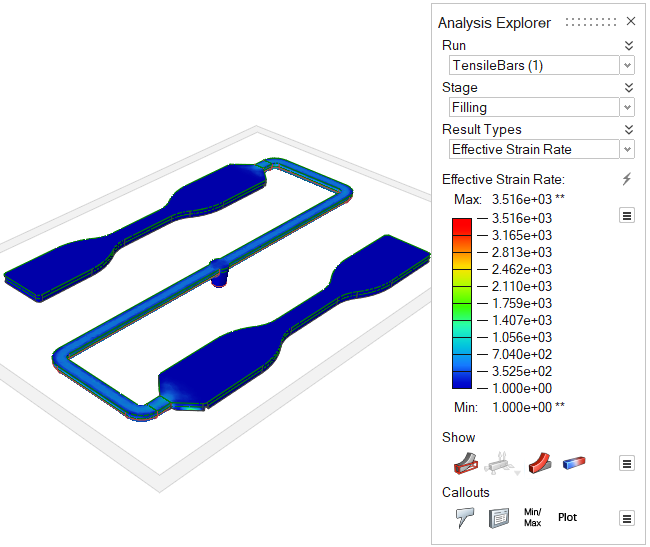 |
| Effective Viscosity | Review the polymer's effective viscosity over time. Effective
viscosity is a function of temperature and strain rate, and
directly affects the material's flow behavior. This result can
help you design gate regions for optimal filling. 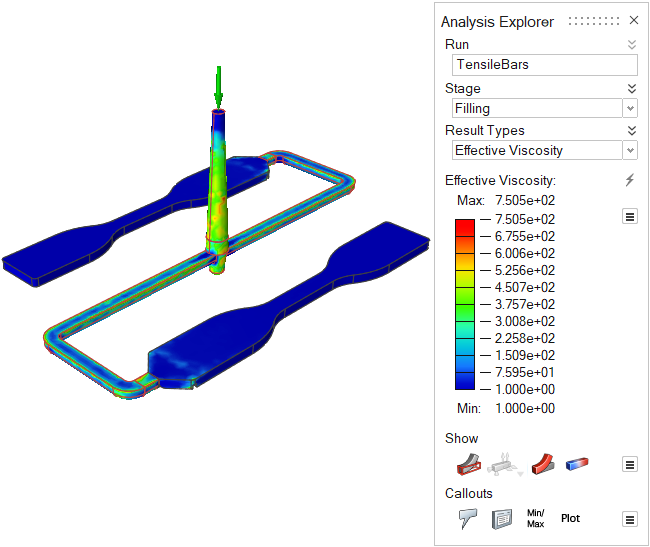 |
| Density | Review the polymer's density over time. Uniform density is
ideal for high quality results.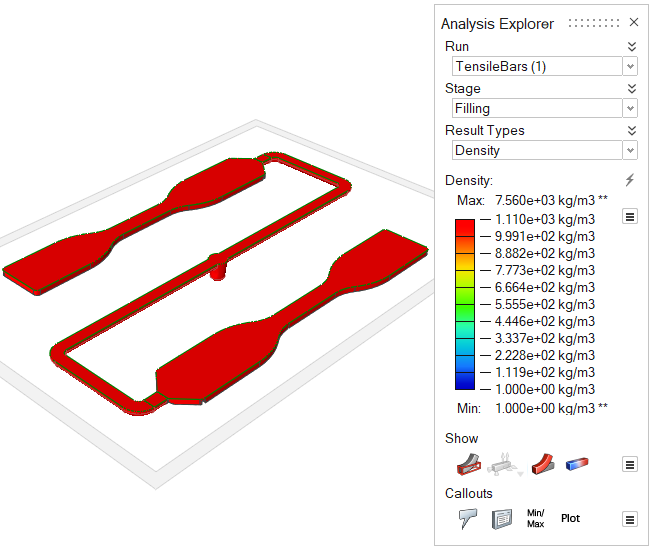 |
| Thickness | Review the thickness of different areas of the part. Local
part thickness affects local strain rates and heat flow. Abrupt
changes in thickness cause uneven cooling, which can lead to
part shrinkage and defects such as sink marks in the final part.
This result can give insight into the entire process.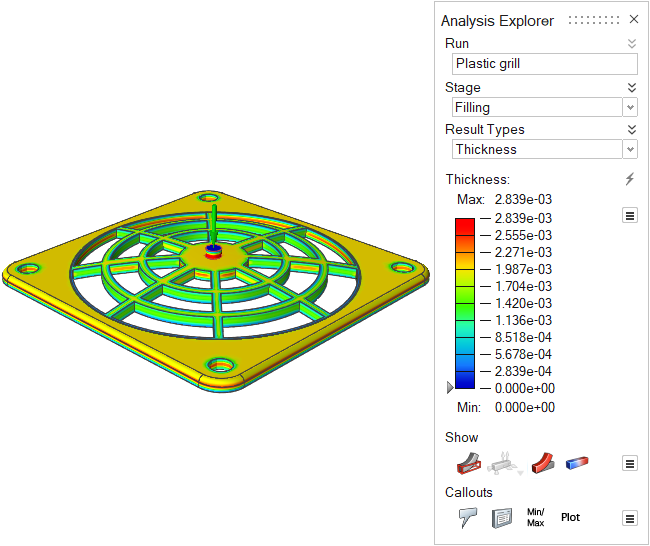 |
| Mold Temperature | Review temperature variances in the mold.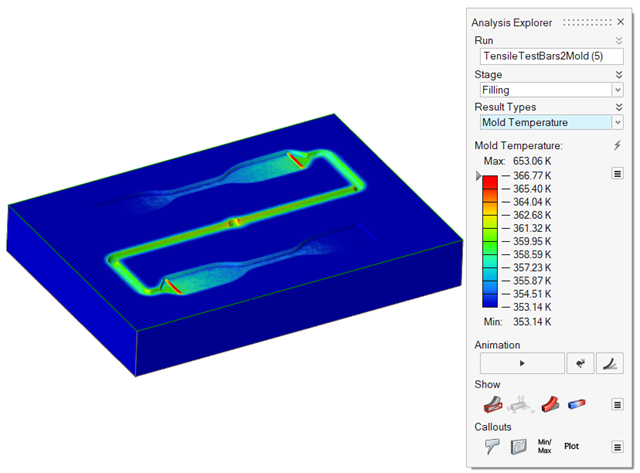 |
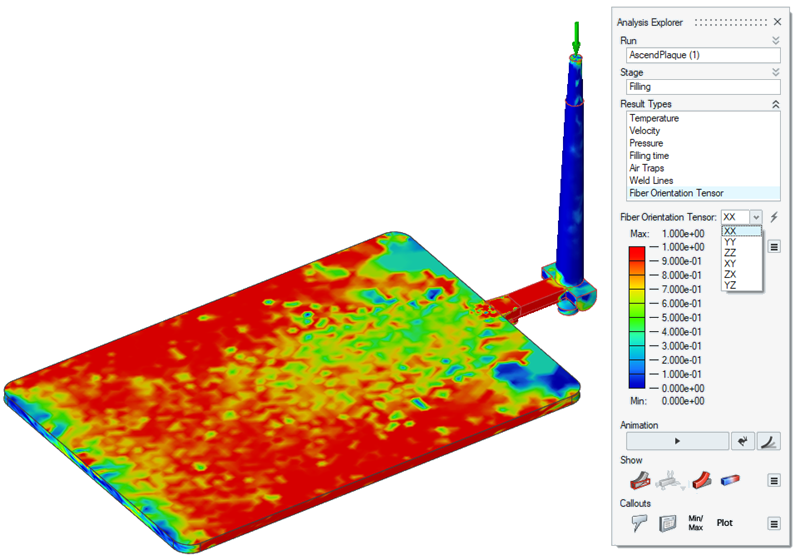
| Fiber Orientation Tensor | Review diagonal and cross products results for the tensors.
The result predicts the fiber orientation tensor for short fiber
reinforced polymers.
 |
Packing Results
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Review temperatures during the packing phase. The temperature
will decrease due to the temperature loss across the mold
walls.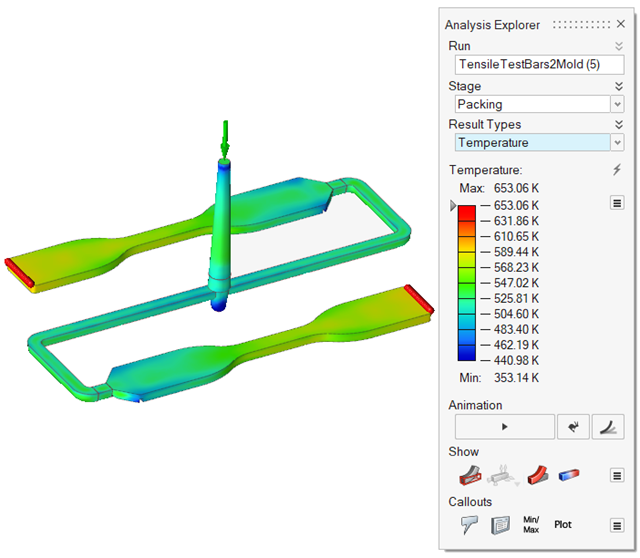 |
| Velocity | Examine velocity during the packing phase. Velocities will
decrease until the fluid stops flowing. |
| Pressure | Consider pressures during the packing phase. These results
are useful to know points where the pressure is less than 0 to
detect areas prone to suffer a sink mark defect.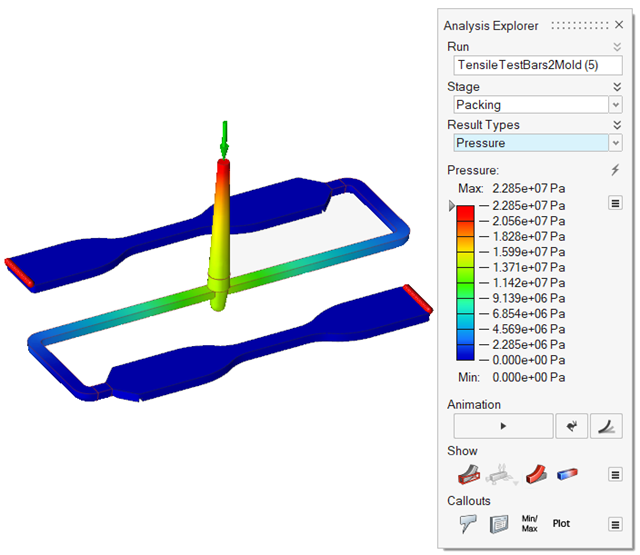 |
| Sink Marks | Detect surface depressions, usually in the thicker sections
of the model, caused by shrinkage during the packing
stage.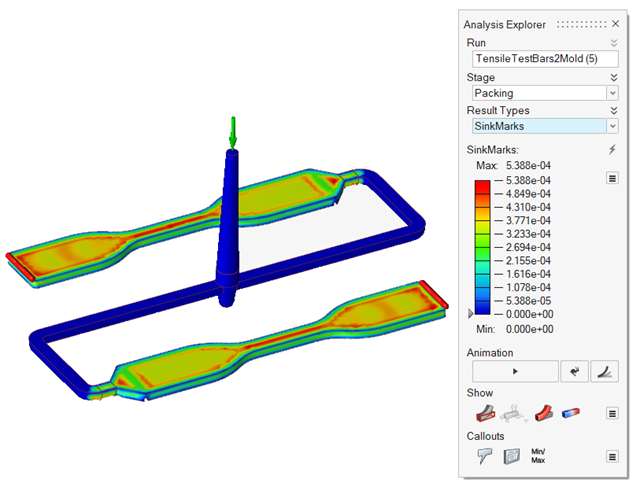 |
| Density | Review changes in the polymer's density over time. Uniform
density is ideal for high quality results. This result can help
pinpoint the causes of such defects as sink marks and
shrinkage.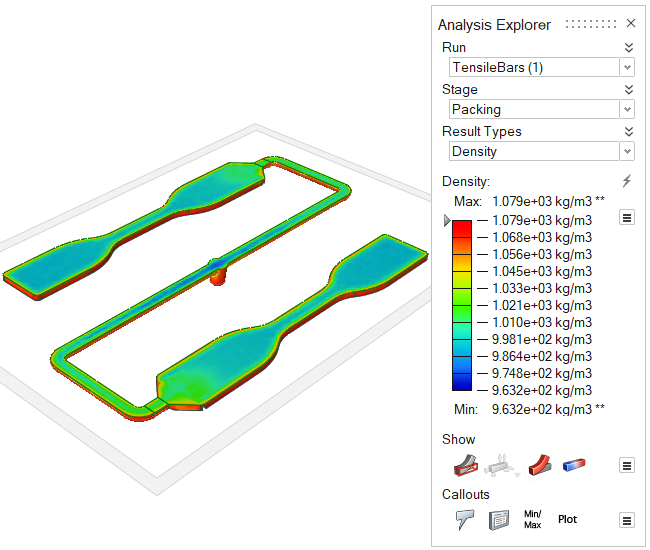 |
| Thickness | Review the thickness of different areas of the part. Local
part thickness affects local strain rates and heat flow. Abrupt
changes in thickness cause uneven cooling, which can lead to
part shrinkage and defects such as sink marks in the final
part. This result can give insight into the entire
process.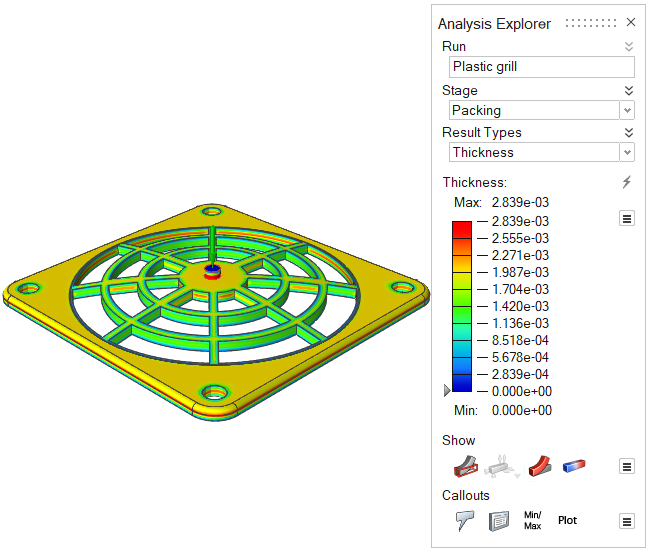 |
| Mold Temperature | Review temperature variances in the mold.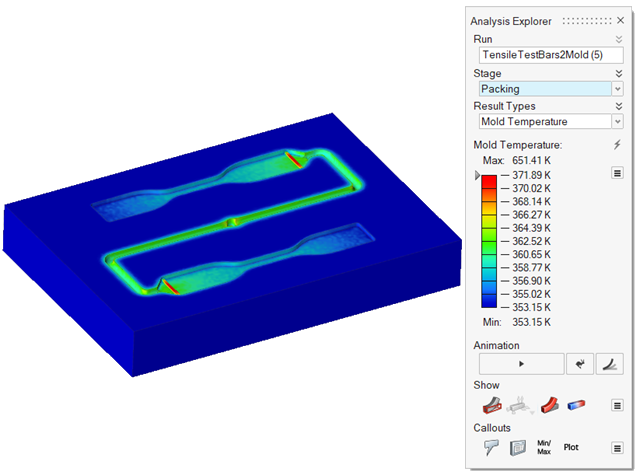 |
Cooling Results
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Examine the temperature evolution once the mold is totally
filled. You can determine the final temperature at which to stop
the cooling phase.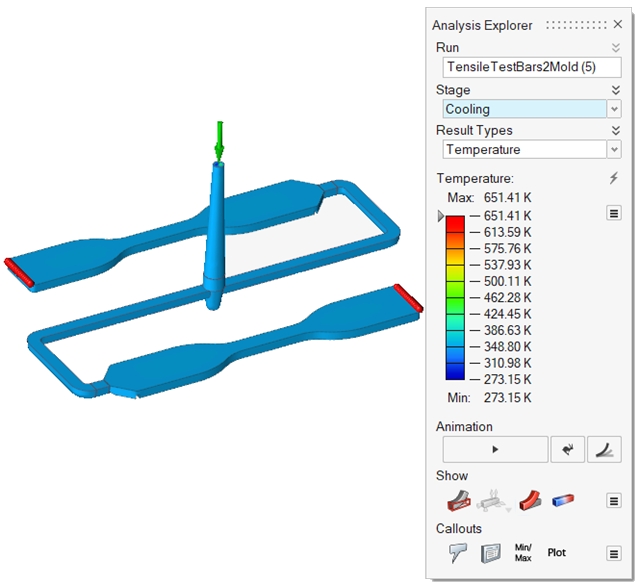 |
| Density | Review changes in the polymer's density over time. Uniform
density is ideal for high quality results. This result can help
pinpoint the causes of such defects as sink marks and shrinkage.
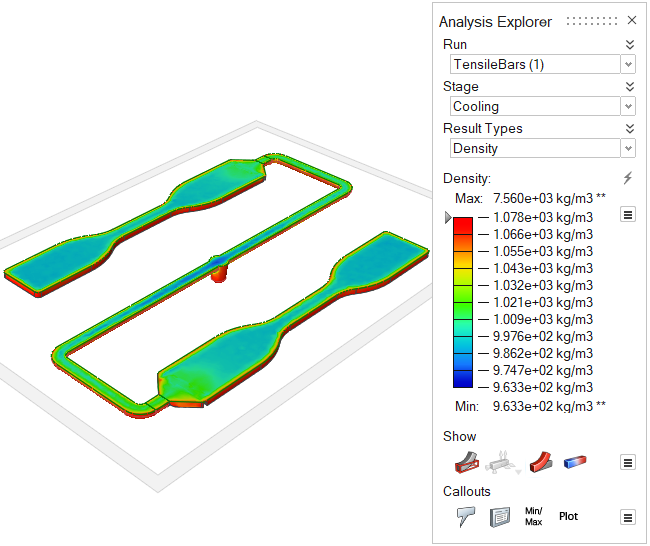 |
| Mold Temperature | Review temperature variances in the mold.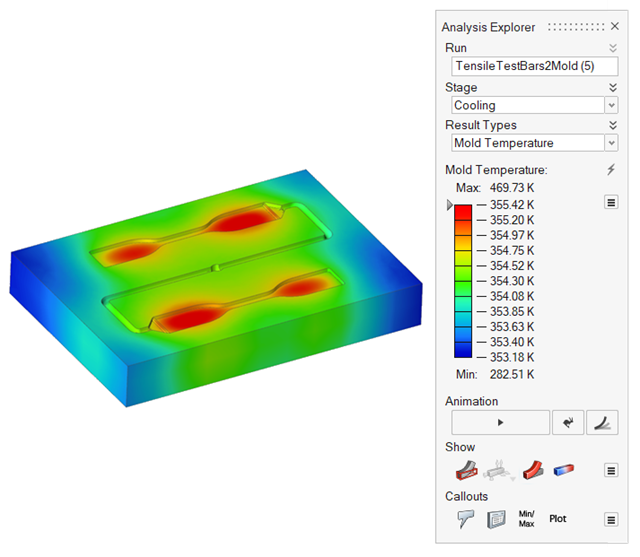 |
Warpage Results
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Displacement | Detect folding, bending, twisting or bowing in the molded
part, which is usually due to non-uniform cooling. The
displacement contour displays how the part is warping so that
you can make the appropriate corrective measures to the cooling
rate, cooling channel design, or process data.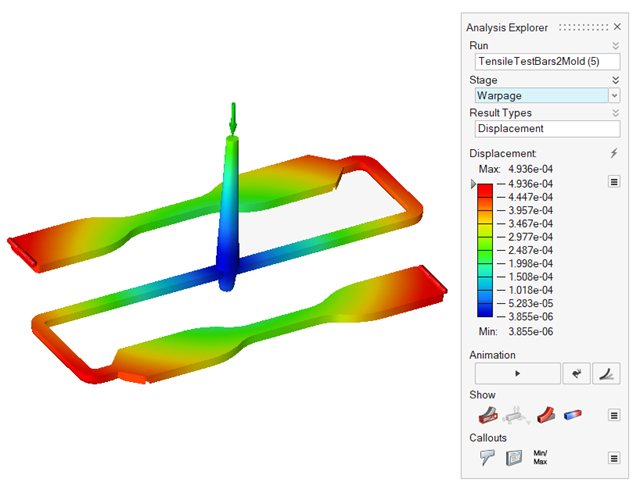 |