Laminates
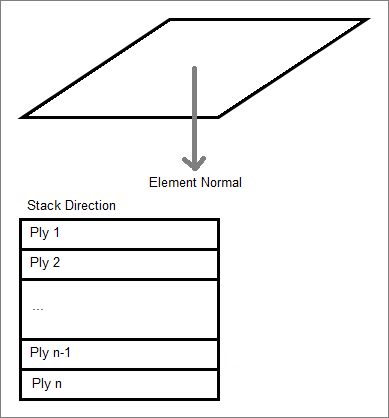
Laminate entities define laminates, which make up a laminated structure by defining the stacking sequence of ply entities that make up the laminated structure.
- Ply Laminates
- Define laminates which make up flat or slightly curved laminated structures.
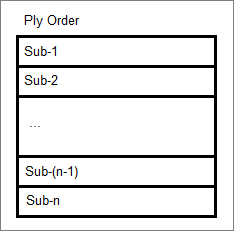
- Sub-Laminates
- Similar to ply laminates in that they also stack ply entities. However, sub-laminates define only a portion of a laminate rather than a complete laminate structure.
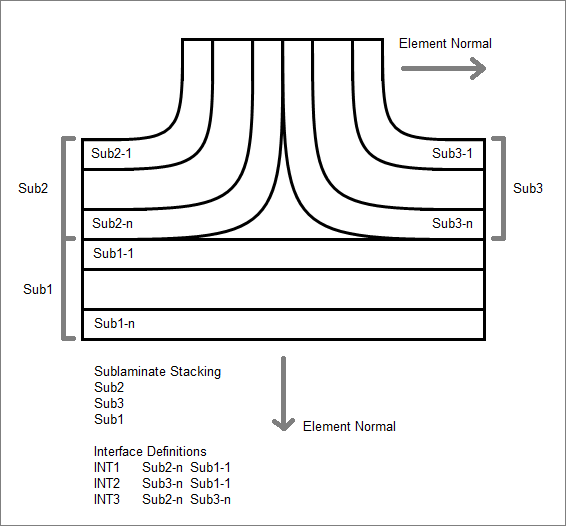
- Interface Laminates
- Define laminates which make up complex laminated structures that wrap around corners.