Time Division Duplex
The duplex separation of downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) is typically done either by using FDD or by using time division duplex (TDD).
Time Division Duplex
Air interface standards using TDD are for example LTE TDD and TD-SCDMA. To specify the TDD configuration of various air interfaces, click , click the Air Interface tab. Under Duplex Separation, from the drop-down list, select Duplex: TDD and click Settings.
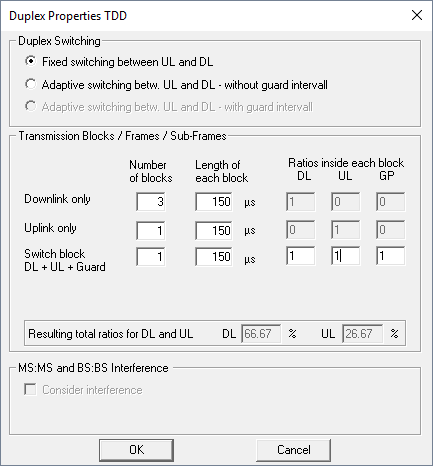
Figure 1. The Duplex Properties TDD dialog.
- Duplex switching
- Switching between downlink and uplink channel in TDD mode can be specified to be fixed or adaptive. The adaptive mode allows switching between downlink and uplink according to the traffic load, either with or without taking into account the guard interval. In case of adaptive switching, always full availability is assumed for each direction (downlink or uplink). Therefore no further specifications are required in this case.
- Transmission Blocks / Frames / Sub-Frames
- Both standards (with switching points in each sub-frame or with switching points
only once or twice per frame) can be defined. Figure 1 shows the
definition of 8 sub-frames completely allocated to the downlink (DL), one
sub-frame completely allocated to the uplink (UL), and one specific sub-frame with
10:2:2 separation between DL:UL:GP where GP stands for guard period. The resulting
overall ratios for downlink and uplink allocation are automatically computed
(depending on the settings) and considered in the network simulation for each
individual modulation and coding scheme.
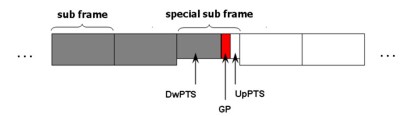
Figure 2. Sketch of a sub frame. - MS : MS and BS : BS interference
- Consider additional interference effects caused by other mobile stations or other base stations, respectively.