Exporting the Platform Mesh in HyperWorks
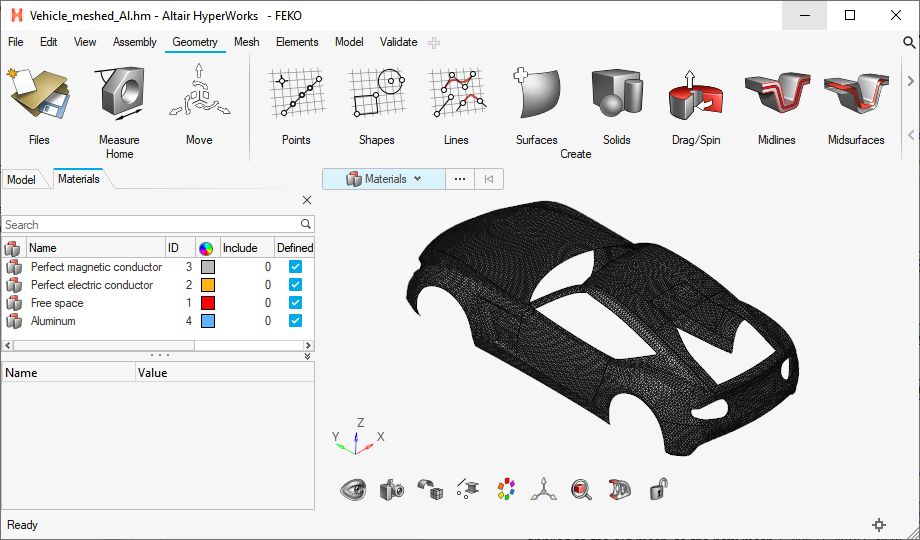
The mesh of the platform is exported to a Feko HyperMesh (.fhm) file which contains the mesh elements, material properties, and assignment data.
See what's new in the latest release.
The Feko Getting Started Guide contains step-by-step instructions on how to get started with Feko.
The Feko Example Guide contains a collection of examples that teaches you Feko concepts and essentials.
Feko is a comprehensive electromagnetic solver with multiple solution methods that is used for electromagnetic field analyses involving 3D objects of arbitrary shapes.
CADFEKO is used to create and mesh the geometry or model mesh, specify the solution settings and calculation requests in a graphical environment.
POSTFEKO, the Feko post processor, is used to display the model (configuration and mesh), results on graphs and 3D views.
EDITFEKO is used to construct advanced models (both the geometry and solution requirements) using a high-level scripting language which includes loops and conditional statements.
One of the key features in Feko is that it includes a broad set of unique and hybridised solution methods. Effective use of Feko features requires an understanding of the available methods.
Feko offers state-of-the-art optimisation engines based on generic algorithm (GA) and other methods, which can be used to automatically optimise the design and determine the optimum solution.
The Feko utilities consist of PREFEKO, OPTFEKO, ADAPTFEKO, the Launcher utility, Updater and the crash reporter.
Feko writes all the results to an ASCII output file .out as well as a binary output file .bof for usage by POSTFEKO. Use the .out file to obtain additional information about the solution.
A large collection of application macros are available for CADFEKO and POSTFEKO.
CADFEKO and POSTFEKO have a powerful, fast, lightweight scripting language integrated into the application allowing you to create models, get hold of simulation results and model configuration information as well as manipulation of data and automate repetitive tasks.
Reference information is provided in the appendix.
CADFEKO and POSTFEKO have a powerful, fast, lightweight scripting language integrated into the application that allows you to create models, get hold of simulation results and model configuration information and much more.
Each geometry and calculation request are entered on a separate line in the .pre and are referred to as cards.
A collection of how-tos are included that covers advanced concepts.
Feko integrates into job scheduling and queuing systems such as Altair PBS Professional, Torque, IBM Platform LSF, Parallelnavi NQS, SLURM and Univa Grid Engine.
A method is presented on how to feed a grounded coplanar waveguide (GCPW) in CADFEKO. The same method can be used to feed a coplanar waveguide (CPW).
A method is presented that allows you to estimate the memory requirements for a model solved using the multilevel fast multipole method (MLFMM).
A method is presented on how to construct a conformal patch antenna in CADFEKO.
A method is presented on how to construct and feed a complementary slotted two-arm spiral antenna in CADFEKO.
The MLFMM is an iterative solution method, and under certain conditions, the iterative solution may fail to converge. Several model or solution settings are presented that could improve the model's convergence behaviour.
The hybrid multilevel fast multipole method (MLFMM) / finite element method (FEM) is an iterative solution method and under certain conditions, the iterative solution may fail to converge. Several model or solution settings are presented that could improve the model's convergence behaviour.
The hybrid method of moments (MoM) / finite element method (FEM) is an iterative solution method, and under certain conditions, the iterative solution may fail to converge. Several model or solution settings are presented that could improve the model's convergence behaviour.
The finite difference time domain (FDTD) is a solution method that may fail to converge under certain conditions. Several model or solution settings are presented that could improve the model's convergence behaviour.
Several tips and tricks are presented to reduce runtime and memory consumption. A few general tips are given as well as solution method-specific tips.
Various methods are presented on how to feed a microstrip line using an infinite planar multilayer substrate in CADFEKO.
A workflow is presented on how to connect an antenna model designed in CADFEKO to a platform model that was meshed with Altair HyperMesh.
The mesh of the platform is exported to a Feko HyperMesh (.fhm) file which contains the mesh elements, material properties, and assignment data.
To ensure mesh connectivity between the antenna mesh and platform mesh in the steps that follow, create a base for the antenna that will protrude and intersect the platform.
The mesh of the platform (.fhm file) is imported into CADFEKO model containing the antenna.
The antenna is placed on the platform and remeshed.
The full model (antenna and platform) is exported to a Feko HyperMesh (.fhm) file.
The platform and antenna base are unioned using the Mesh Boolean tool and remeshed.
The connected antenna mesh and platform mesh are imported into CADFEKO and simulated.
When meshing a model, you can either use the automatic meshing algorithm to calculate the appropriate mesh settings or you can specify the mesh sizes. When you specify the mesh sizes, the mesh sizes should adhere to certain guidelines.
Feko makes use of a local peak SAR algorithm.
Control the execution of Feko by specifying the memory management and environment variables.
The .mat file, .lud file and .rhs file are not generated by default, but can be read externally.
Feko integrates with various products within Altair Simulation Products such as HyperStudy. Integration with third-party products is also supported through the powerful scripting and plug-in infrastructure.
Use the correct structure, convention and syntax for a SPICE circuit definition in Feko.
View the list of commonly used acronyms in Feko.
Feko creates and uses many different file types. It is useful to know what is stored in the various files and weather they were created by Feko and if it is safe to delete them. The files are grouped as either native files that have been created by Feko or non-native files that are supported by Feko. Non-native files are often exported by Feko even if the formats are not under the control of the Feko development team.
A list of notes, errors and warnings are provided as reference and to provide more information regarding the reason for the message and how to resolve the problem in the model.
Reference information is provided in the appendix.
A collection of how-tos are included that covers advanced concepts.
A workflow is presented on how to connect an antenna model designed in CADFEKO to a platform model that was meshed with Altair HyperMesh.
The mesh of the platform is exported to a Feko HyperMesh (.fhm) file which contains the mesh elements, material properties, and assignment data.
The mesh of the platform is exported to a Feko HyperMesh (.fhm) file which contains the mesh elements, material properties, and assignment data.
(c) 2021. Altair Engineering Inc. All Rights Reserved.