Microstrip Port
Different configurations using a microstrip port are considered.
The first configuration considered is to define a microstrip port on the full width of the microstrip line. For the second and third configurations, a feed structure is created using polygons to decrease the width of the microstrip port.
Narrow Version
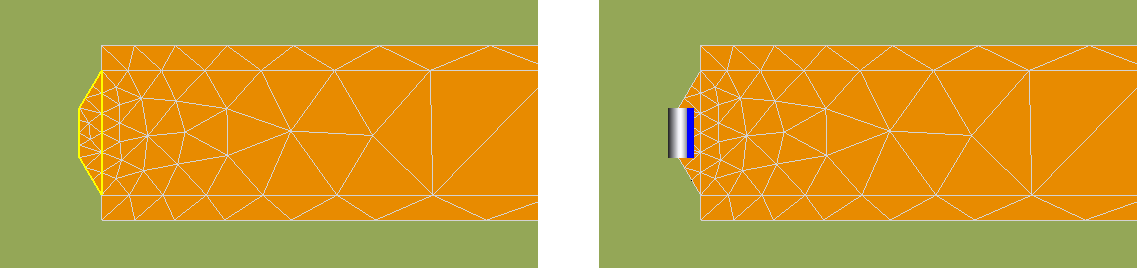
Figure 1. Top view of the partial microstrip line. On the left, the feed structure is indicated in yellow. To the right, the microstrip port is added to the feed structure.