Creating Data Extract from Text
The Text connector allows the retrieval and processing of delimited Text files (such as CSV, TSV, and so on), either from a disk or from a defined URL.
Steps:
1. On the New Data Extract page, select Text in the Connector drop-down list.
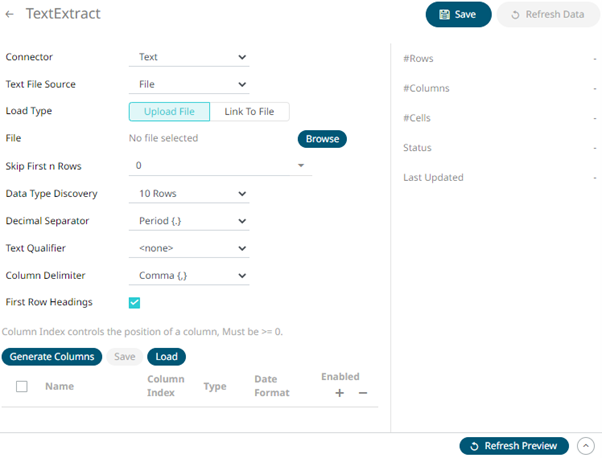
2. Select the text file source:
· Text
Enter the text block to be parsed.
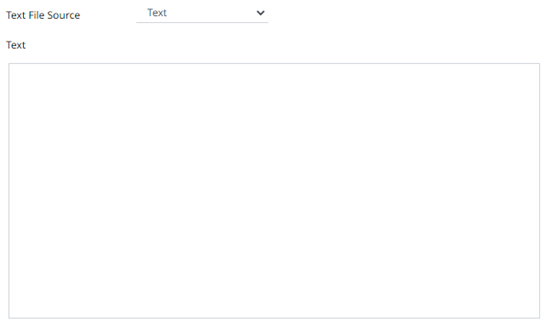
· File
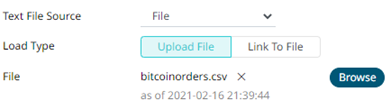
You can either:
¨ Upload a data source snapshot by clicking
Upload File  then Browse
then Browse  to
browse to the file source.
to
browse to the file source.
After selecting the file, it is displayed with the timestamp of the snapshot.
To
change the data source, click  then
Browse
then
Browse  to browse to a new version of
the file.
to browse to a new version of
the file.
¨ Link to a data source file by clicking
Link to File  and entering a Text File Path.
and entering a Text File Path.
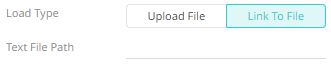
Ensure that in a cluster, you need to use a a shared path, or put it on every node and use a path that resolves on every node. You can update its contents whenever you want.
· WebURL
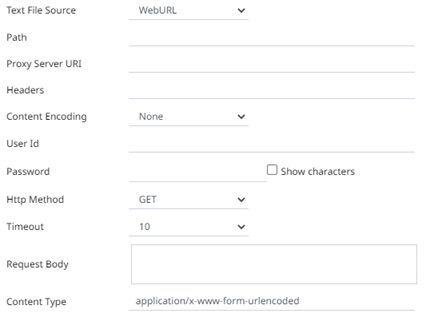
The dialog changes slightly to allow specification of the following:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Path |
The absolute path including the HTTP where the Text file is located. |
|
Proxy Server URI |
The HTTP Proxy setting that will allow the Text connector to reach the endpoint |
|
Headers |
· Headers are separated by a comma · Each Header is entered as Name = Value, where Name and Value can be enclosed in double quotes to allow inclusion of any character except for double quotes · Name and Value can also be left unquoted, in which case they may not include comma or equals characters |
|
Content Encoding |
Select the Content Encoding with the HTTP Header: None, GZip, Deflate, or GZip and Deflate |
|
User Id |
The user Id that will be used to connect to the Text service. |
|
Password |
The password to connect to the Text service. |
|
Http Method |
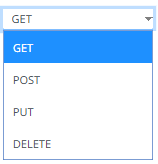
Select the HTTP Method to map any of the following operations to HTTP requests
· GET – retrieve information · POST – create or update an entity · PUT – replace an existing entity · DELETE – remove a request |
|
Timeout |
The length of time to wait for the server response (10 to 300). Default is 10. |
|
Request Body |
The Request Body for HTTP POST. |
|
Content Type |
The required Content Type. Default is application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
The standard settings controlling how the text file is parsed, is listed.
These include:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Skip First N Rows |
Specifies the number of rows that will be skipped. |
|
Data Type Discovery |
Specifies how many rows from the text file should be used when automatically determining the data types of the resulting columns. |
|
Decimal Separator |
Select either the dot (.) or comma (,) as the decimal separator. |
|
Text Qualifier |
Specifies if fields are enclosed by text qualifiers, and if present to ignore any column delimiters within these text qualifiers. |
|
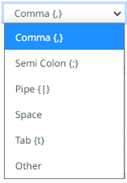
Column Delimiter |
Specifies the column delimiter to be used when parsing the text file.
|
|
First Row Headings |
Determines if the first row should specify the retrieved column headings, and not be used in data discovery. |
3. Click  to the fetch the schema based
on the connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with
the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input
data source is populated and the Save button is enabled.
to the fetch the schema based
on the connection details. Consequently, the list of columns with
the data type found from inspecting the first ‘n’ rows of the input
data source is populated and the Save button is enabled.
4. You can also opt to load or save a copy of the column definition.
5. Click  . A new column entry displays. Enter
or select the following properties:
. A new column entry displays. Enter
or select the following properties:
|
Property |
Description |
|
Name |
The column name of the source schema. |
|
Column Index |
The column index controls the position of a column. Must be >= 0. |
|
Type |
The data type of the column. Can be a Text, Numeric, or Time |
|
Date Format |
The format when the data type is Time. |
|
Enabled |
Determines whether the message should be processed. |
To
delete a column, check its  or all the column entries, check
the topmost
or all the column entries, check
the topmost  ,
then click
,
then click  .
.
6. Click  to save and display the details
of the data extract.
to save and display the details
of the data extract.
7. Click  then
then  to display the data preview.
to display the data preview.