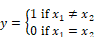
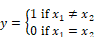
Block Category: Boolean
Inputs: Real, complex, or fixed-point scalars, or vectors or matrices.
On the input connector tabs, “l” represents the x1 and “r” represents the x2.
Description: The != block produces an output signal of 1 if and only if the two scalar input signals are not equal. On the connector tabs, “l” represents x1 and “r” represents x2.
Right-click the != block, to assign a different function to the block.
1. Comparing constants
Consider a variable y such that:
If t ≠ 0.5 then y = cos(t); else y = 0
where t is simulation time realized as:
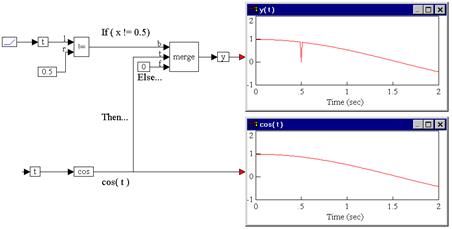
Until the value of t reaches 0.5, the Boolean inequality t ≠ 0.5 evaluates to true, and y takes on a value of cos(t). At t = 0.5 sec, the Boolean inequality evaluates to false, and at the very next time step, returns to true, and remains true for the duration of the simulation. Consequently, at the moment t = 0.5 sec, y takes on the value of 0, and at every other point, y is equal to cos(t).