PID
This block is a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller.
![]()
Library
Dynamical
Description
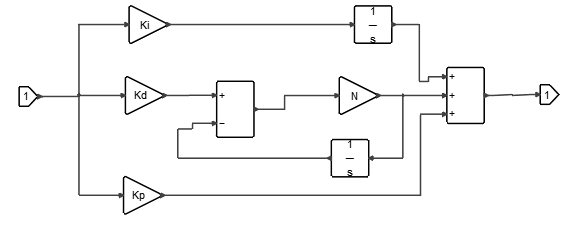
The PID block implements a PID controller. The PID controller calculation (algorithm) involves three separate parameters: Proportional, Integral and Derivative. The Proportional value determines the reaction to the current error, the Integral value determines the reaction based on the sum of recent errors, and the Derivative value determines the reaction to the rate at which the error has been changing. The weighted sum of these three actions is used to adjust the process via a control element such as the position of a control valve or the power supply of a heating element.
Parameters

| Name | Label | Description | Data Type | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Kp | Proportional gain | Real value. The value of the gain that multiplies the error. | Scalar | |
Ki | Integral gain | Real value. The value of the integral time of the error. | Scalar | |
Kd | Derivative gain | Real value. The value of the derivative time of the error. | Scalar | |
N | Filter coefficient | Real value. The value of the filter coefficient, which determines the pole location of the filter in the derivative action. | Scalar |
Ports
| Name | Type | Description | IO Type | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Port 1 | explicit | output | 1 | |
Port 2 | explicit | input | 1 |
Advanced Properties
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
always active | yes | |
direct-feedthrough | yes | PID block is direct-feedthrough unless the proportional gain (Kp) is zero (0). |
zero-crossing | no | |
mode | no | |
continuous-time state | no | |
discrete-time state | no |