Laminar Flow Through a Pipe with Species Transport
In this application, AcuSolve is used to simulate the transport of a passive scalar species in a fully developed laminar flow. AcuSolve results are compared with analytical results as described in Kays and Crawford (1993). The close agreement of AcuSolve results with analytical results validates the ability of AcuSolve to model cases with species transport.
Problem Description
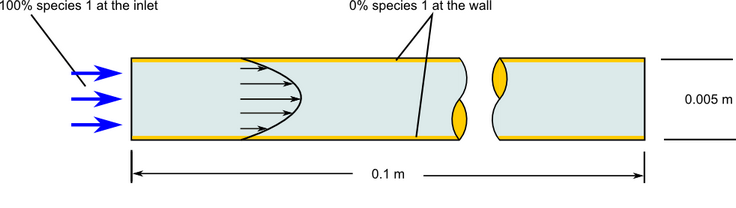
Figure 1. Critical Dimensions and Parameters for Simulating Laminar Flow Through a Pipe with Species Transport

Figure 2. Mesh used for Simulating Laminar Flow Through a Pipe with Species Transport
AcuSolve Results
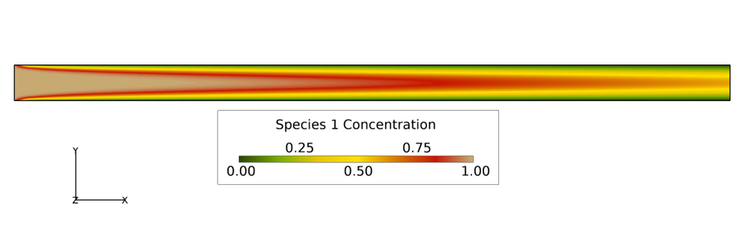
Figure 3. Contours of Concentration for Species 1
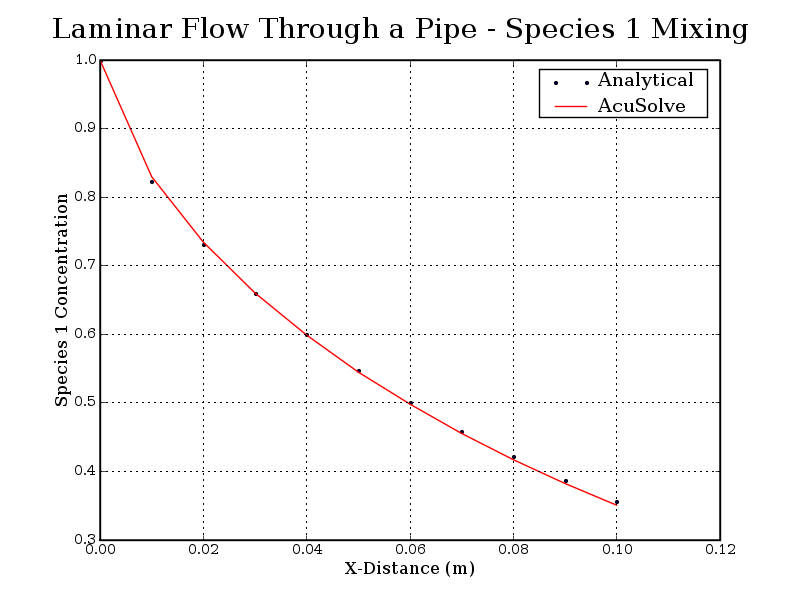
Figure 4. Species 1 Concentration Plotted Against Distance from the Pipe Inlet
| Distance along pipe (m) | Analytical species 1 fraction | AcuSolve species 1 fraction | Percent deviation from analytical |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0000* | 1.0000 | 0.00 |
| 0.01 | 0.8225 | 0.8298 | 0.90 |
| 0.02 | 0.7308 | 0.7344 | 0.49 |
| 0.03 | 0.6593 | 0.6603 | 0.15 |
| 0.04 | 0.5992 | 0.5988 | 0.06 |
| 0.05 | 0.5469 | 0.5448 | 0.38 |
| 0.06 | 0.5006 | 0.4981 | 0.49 |
| 0.07 | 0.4589 | 0.4554 | 0.78 |
| 0.08 | 0.4212 | 0.4171 | 0.98 |
| 0.09 | 0.3869 | 0.3824 | 1.15 |
| 0.1 | 0.3555 | 0.3507 | 1.35 |
* The theoretical species fraction at the inlet is shown rather than the analytical. In order for the analytical solution to correspond exactly with the theoretical results, additional terms in the series summation would need to be evaluated.
Summary
The AcuSolve solution compares well with analytical results for flow through a pipe with species transport. In this application, a fully developed laminar profile is achieved by enforcing periodic constraints on the pressure and velocity fields. The spatially developing species field is achieved by not enforcing periodicity and allowing the concentration to evolve along the full length of the model. The change in concentration along the pipe length is due to advection in the streamwise direction and diffusion of the species to the outer walls where the concentration is zero. The AcuSolve solution for fraction of species 1 is within 1.35 percent of analytical results.
Simulation Settings for Laminar Flow Through a Pipe with Species Mixing
AcuConsole database file: <your working directory>\pipe_laminar_species\pipe_laminar_species.acs.
Global
- Problem Description
- Analysis type - Steady State
- Species equation - Advective Diffusive
- Num. species - 1
- Turbulence equation - Laminar
- Auto Solution Strategy
- Relaxation factor - 0.2
- Material Model
- Species1
- Density - 1.0 kg/m3
- Viscosity - 1.0e-5 kg/m-sec
- Diffusivity
- 1
- Diffusivity - 1.43e-5 kg/m-sec
- 1
Model
- Species1
- Volumes
- Fluid
- Element Set
- Material model - Species1
- Element Set
- Fluid
- Surfaces
- Inflow
- Simple Boundary Condition - (disabled to allow for periodic conditions to be set)
- Advanced Options
- Nodal Boundary Conditions
- Species 1
- Type - Constant
- Constant value - 1.0
- Species 1
- Integrated Boundary Conditions
- Mass Flux
- Type - Constant
- Constant value - 1.96e-05 kg/sec
- Mass Flux
- Nodal Boundary Conditions
- Outflow
- Simple Boundary Condition - (disabled to allow for periodic conditions to be set)
- Wall
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Type - Wall
- Species 1 BC type - Value
- Species 1 - 0.0
- Simple Boundary Condition
- Inflow
- Periodics
- Periodic 1
- Individual Periodic BCs
- Velocity
- Type - Periodic
- Pressure
- Type - Single Unknown Offset
- Velocity
- Individual Periodic BCs
- Periodic 1
References
W. M. Kays and M. E. Crawford. "Convective Heat and Mass Transfer", 3rd Edition. pp. 126-134. McGraw-Hill Book Co., Inc. New York. 1993.